RNA Seq profiling reveals a novel expression pattern of TGF-β target genes in human blood eosinophils
- PMID: 26112417
- PMCID: PMC6208316
- DOI: 10.1016/j.imlet.2015.06.012
RNA Seq profiling reveals a novel expression pattern of TGF-β target genes in human blood eosinophils
Abstract
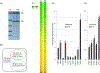
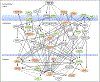
Despite major advances in our understanding of TGF-β signaling in multiple cell types, little is known about the direct target genes of this pathway in human eosinophils. These cells constitute the major inflammatory component present in the sputum and lung of active asthmatics and their numbers correlate well with disease severity. During the transition from acute to chronic asthma, TGF-β levels rise several fold in the lung which drives fibroblasts to produce extracellular matrix (ECM) and participate in airway and parenchymal remodeling. In this report, we use purified blood eosinophils from healthy donors and analyze baseline and TGF-β responsive genes by RNA Seq, and demonstrate that eosinophils (PBE) express 7981 protein-coding genes of which 178 genes are up-regulated and 199 genes are down-regulated by TGF-β. While 18 target genes have been previously associated with asthma and eosinophilic disorders, the vast majority have been implicated in cell death and survival, differentiation, and cellular function. Ingenuity pathway analysis revealed that 126 canonical pathways are activated by TGF-β including iNOS, TREM1, p53, IL-8 and IL-10 signaling. As TGF-β is an important cytokine for eosinophil function and survival, and pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis, our results represent a significant step toward the identification of novel TGF-β responsive genes and provide a potential therapeutic opportunity by selectively targeting relevant genes and pathways.
Keywords: Asthma; Blood; Eosinophils; Gene expression; Human; RNA-Seq; TGF-β.
Copyright © 2015 European Federation of Immunological Societies. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human eosinophils have an intact Smad signaling pathway leading to a major transforming growth factor-beta target gene expression.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2007;142(4):309-17. doi: 10.1159/000097500. Epub 2006 Nov 27. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17135762
-
Asthmatic Eosinophils Alter the Gene Expression of Extracellular Matrix Proteins in Airway Smooth Muscle Cells and Pulmonary Fibroblasts.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 7;23(8):4086. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084086. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35456903 Free PMC article.
-
Activation and transforming growth factor-beta production in eosinophils by hyaluronan.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2000 Oct;23(4):444-51. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.23.4.3875. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 11017908
-
Transforming growth factor β and severe asthma: a perfect storm.Respir Med. 2014 Oct;108(10):1409-23. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2014.08.008. Epub 2014 Sep 6. Respir Med. 2014. PMID: 25240764 Review.
-
The regulatory role of TGF-beta in airway remodeling in asthma.Immunol Cell Biol. 2007 Jul;85(5):348-56. doi: 10.1038/sj.icb.7100044. Epub 2007 Feb 27. Immunol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17325694 Review.
Cited by
-
α-Arrestins and Their Functions: From Yeast to Human Health.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 30;23(9):4988. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094988. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reuse of public, genome-wide, murine eosinophil expression data for hypotheses development.J Leukoc Biol. 2018 Jul;104(1):185-193. doi: 10.1002/JLB.1MA1117-444R. Epub 2018 May 14. J Leukoc Biol. 2018. PMID: 29758095 Free PMC article.
-
IL-5-stimulated eosinophils adherent to periostin undergo stereotypic morphological changes and ADAM8-dependent migration.Clin Exp Allergy. 2017 Oct;47(10):1263-1274. doi: 10.1111/cea.12934. Epub 2017 May 5. Clin Exp Allergy. 2017. PMID: 28378503 Free PMC article.
-
Mepolizumab Attenuates Airway Eosinophil Numbers, but Not Their Functional Phenotype, in Asthma.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017 Dec 1;196(11):1385-1395. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201611-2234OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017. PMID: 28862877 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Translation and Signaling in Human Eosinophils.Front Med (Lausanne). 2017 Sep 19;4:150. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2017.00150. eCollection 2017. Front Med (Lausanne). 2017. PMID: 28971096 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Batra V, Musani AI, Hastie AT, Khurana S, Carpenter KA, Zangrilli JG, Peters SP (2004) Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid concentrations of transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1, TGF-beta2, interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 after segmental allergen challenge and their effects on alpha-smooth muscle actin and collagen III synthesis by primary human lung fibroblasts. Clin Exp Allergy 34:437–444. - PubMed
-
- Halwani R, Al-Muhsen S, Al-Jahdali H, Hamid Q (2011) Role of transforming growth factor-β in airway remodeling in asthma. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 44:127–133. - PubMed
-
- Makinde T, Murphy RF, Agrawal DK (2007) The regulatory role of TGF-beta in airway remodeling in asthma. Immunol Cell Biol 85:348–356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

