Bee venom ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced memory loss by preventing NF-kappaB pathway
- PMID: 26112466
- PMCID: PMC4501073
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-015-0344-2
Bee venom ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced memory loss by preventing NF-kappaB pathway
Abstract
Background: Accumulation of beta-amyloid and neuroinflammation trigger Alzheimer's disease. We previously found that lipopolysaccharide (LPS) caused neuroinflammation with concomitant accumulation of beta-amyloid peptides leading to memory loss. A variety of anti-inflammatory compounds inhibiting nuclear factor kappaB (NF-κB) activation have showed efficacy to hinder neuroinflammation and amyloidogenesis. We also found that bee venom (BV) inhibits NF-κB.
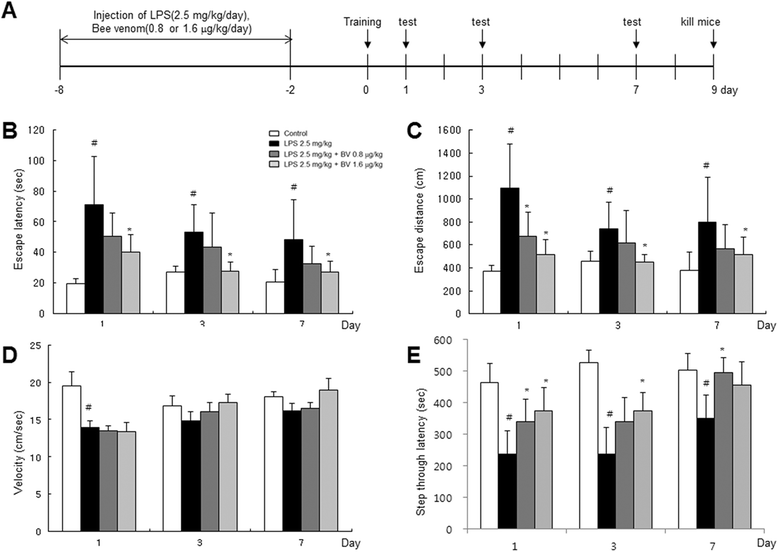
Methods: A mouse model of LPS-induced memory loss used administration of BV (0.8 and 1.6 μg/kg/day, i.p.) to ICR mice for 7 days before injection of LPS (2.5 mg/kg/day, i.p.). Memory loss was assessed using a Morris water maze test and passive avoidance test. For in vitro study, we treated BV (0.5, 1, and 2 μg/mL) to astrocytes and microglial BV-2 cells with LPS (1 μg/mL).
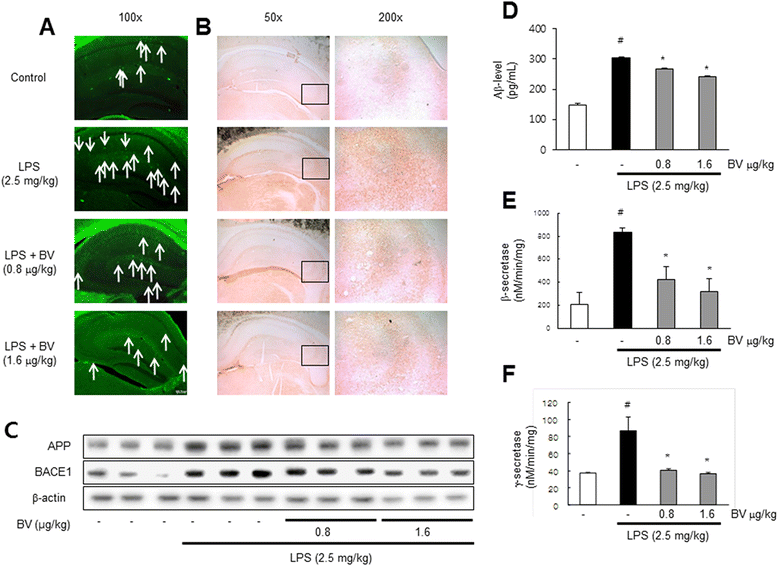
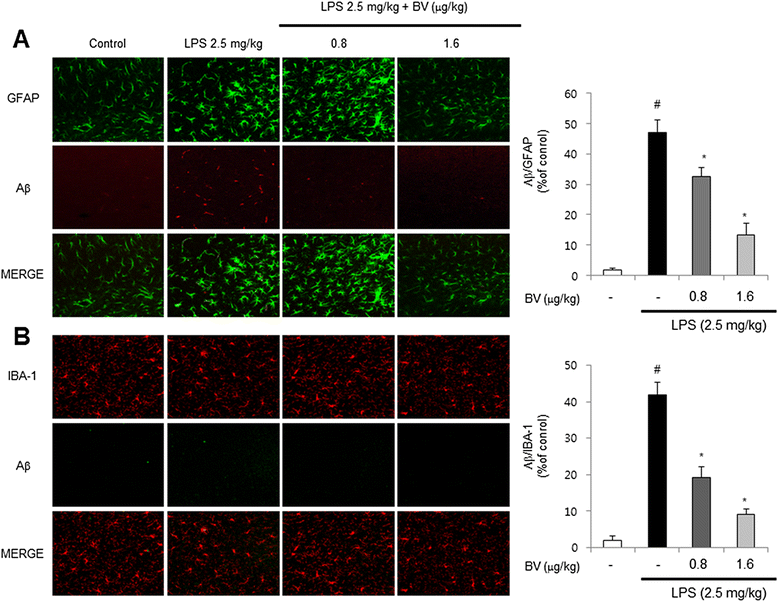
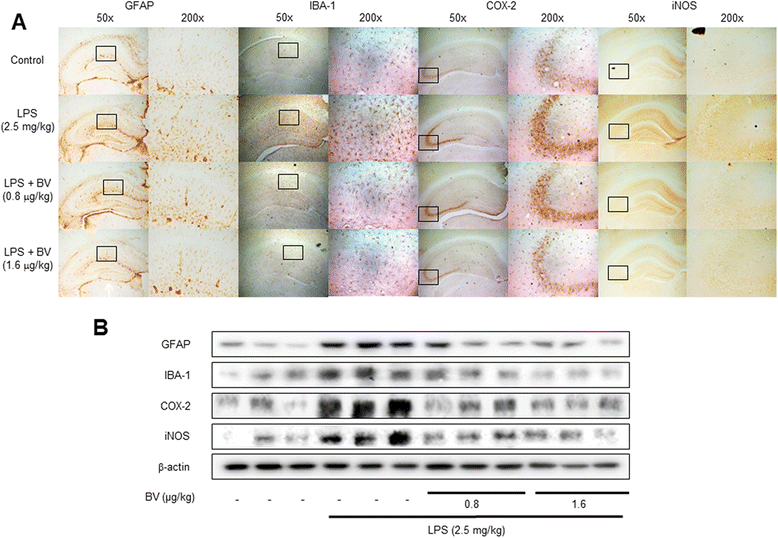
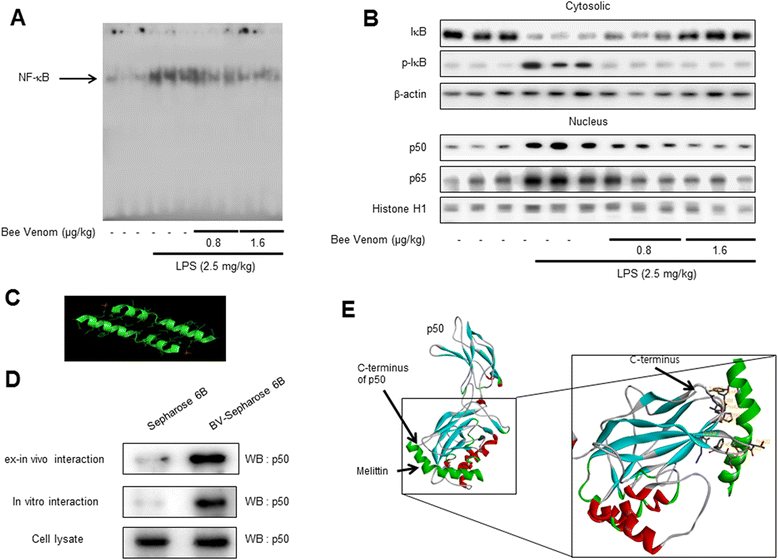
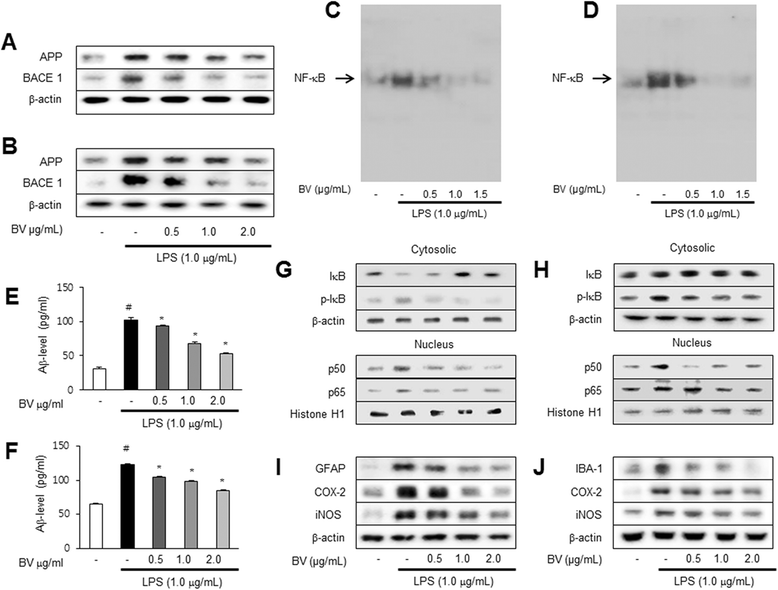
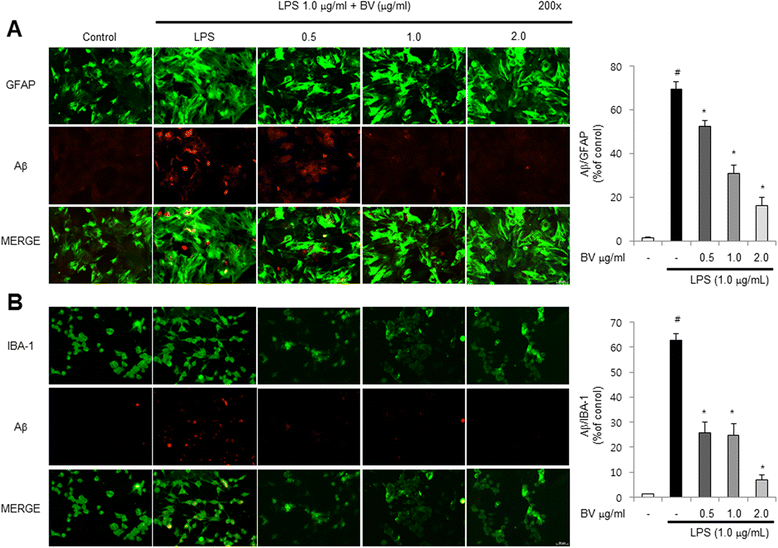
Results: We found that BV inhibited LPS-induced memory loss determined by behavioral tests as well as cell death. BV also inhibited LPS-induced increases in the level of beta-amyloid (Aβ), β-and γ-secretases activities, NF-κB and its DNA-binding activity and expression of APP, and BACE1 and neuroinflammation proteins (COX-2, iNOS, GFAP and IBA-1) in the brain and cultured cells. In addition, pull-down assay and molecular modeling showed that BV binds to NF-κB.
Conclusions: BV attenuates LPS-induced amyloidogenesis, neuroinflammation, and therefore memory loss via inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway. Thus, BV could be useful for treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibitory effect of 4-O-methylhonokiol on lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation, amyloidogenesis and memory impairment via inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB in vitro and in vivo models.J Neuroinflammation. 2012 Feb 19;9:35. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-35. J Neuroinflammation. 2012. PMID: 22339795 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effect of punicalagin on lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and memory impairment via inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB.Neuropharmacology. 2017 May 1;117:21-32. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.01.025. Epub 2017 Jan 26. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28132781
-
Inhibitory effect of ent-Sauchinone on amyloidogenesis via inhibition of STAT3-mediated NF-κB activation in cultured astrocytes and microglial BV-2 cells.J Neuroinflammation. 2014 Jul 2;11:118. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-11-118. J Neuroinflammation. 2014. PMID: 24985096 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB as a Key Mediator of Brain Inflammation in Alzheimer's Disease.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2019;18(1):3-10. doi: 10.2174/1871527316666170807130011. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2019. PMID: 28782486 Review.
-
Anti-Neuroinflammatory Potential of Polyphenols by Inhibiting NF-κB to Halt Alzheimer's Disease.Curr Pharm Des. 2021;27(3):402-414. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666201118092422. Curr Pharm Des. 2021. PMID: 33213314 Review.
Cited by
-
Insamgobonhwan Protects Neuronal Cells from Lipid ROS and Improves Deficient Cognitive Function.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jan 31;11(2):295. doi: 10.3390/antiox11020295. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35204177 Free PMC article.
-
K284-6111 alleviates memory impairment and neuroinflammation in Tg2576 mice by inhibition of Chitinase-3-like 1 regulating ERK-dependent PTX3 pathway.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Nov 22;17(1):350. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-02022-w. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 33222690 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the effect of three licorice varieties on cognitive improvement via an amelioration of neuroinflammation in lipopolysaccharide-induced mice.Nutr Res Pract. 2018 Jun;12(3):191-198. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2018.12.3.191. Epub 2018 Apr 10. Nutr Res Pract. 2018. PMID: 29854324 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory signaling pathways in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease with inhibitors, natural products and metabolites (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2023 Nov;52(5):111. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2023.5314. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Int J Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37800614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rosuvastatin alleviates high-salt and cholesterol diet-induced cognitive impairment in rats via Nrf2-ARE pathway.Redox Rep. 2018 Dec;23(1):168-179. doi: 10.1080/13510002.2018.1492774. Redox Rep. 2018. PMID: 29961403 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

