Comparative Analysis of the Shared Sex-Determination Region (SDR) among Salmonid Fishes
- PMID: 26112966
- PMCID: PMC4524489
- DOI: 10.1093/gbe/evv123
Comparative Analysis of the Shared Sex-Determination Region (SDR) among Salmonid Fishes
Abstract
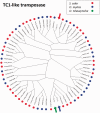
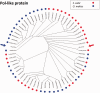
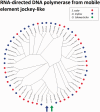
Salmonids present an excellent model for studying evolution of young sex-chromosomes. Within the genus, Oncorhynchus, at least six independent sex-chromosome pairs have evolved, many unique to individual species. This variation results from the movement of the sex-determining gene, sdY, throughout the salmonid genome. While sdY is known to define sexual differentiation in salmonids, the mechanism of its movement throughout the genome has remained elusive due to high frequencies of repetitive elements, rDNA sequences, and transposons surrounding the sex-determining regions (SDR). Despite these difficulties, bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) library clones from both rainbow trout and Atlantic salmon containing the sdY region have been reported. Here, we report the sequences for these BACs as well as the extended sequence for the known SDR in Chinook gained through genome walking methods. Comparative analysis allowed us to study the overlapping SDRs from three unique salmonid Y chromosomes to define the specific content, size, and variation present between the species. We found approximately 4.1 kb of orthologous sequence common to all three species, which contains the genetic content necessary for masculinization. The regions contain transposable elements that may be responsible for the translocations of the SDR throughout salmonid genomes and we examine potential mechanistic roles of each one.
Keywords: comparative genomics; retrotransposition; salmonid; sex-chromsome; sex-determination; transposable element.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Molecular Biology and Evolution.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Lessons from an unusual vertebrate sex-determining gene.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2021 Aug 30;376(1832):20200092. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2020.0092. Epub 2021 Jul 12. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34247499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic Instability of the Sex-Determining Locus in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar).G3 (Bethesda). 2015 Sep 22;5(11):2513-22. doi: 10.1534/g3.115.020115. G3 (Bethesda). 2015. PMID: 26401030 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the sex chromosomes of brown trout (Salmo trutta) and their comparison with the corresponding chromosomes in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) and rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss).Cytogenet Genome Res. 2011;133(1):25-33. doi: 10.1159/000323410. Epub 2011 Jan 20. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2011. PMID: 21252487
-
Comparative genome analysis of the primary sex-determining locus in salmonid fishes.Genome Res. 2003 Feb;13(2):272-80. doi: 10.1101/gr.578503. Genome Res. 2003. PMID: 12566405 Free PMC article.
-
The sex determining loci and sex chromosomes in the family salmonidae.Sex Dev. 2009;3(2-3):78-87. doi: 10.1159/000223073. Epub 2009 Aug 10. Sex Dev. 2009. PMID: 19684453 Review.
Cited by
-
A nonfunctional copy of the salmonid sex-determining gene (sdY) is responsible for the "apparent" XY females in Chinook salmon, Oncorhynchus tshawytscha.G3 (Bethesda). 2022 Feb 4;12(2):jkab451. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkab451. G3 (Bethesda). 2022. PMID: 35100376 Free PMC article.
-
Do Ty3/Gypsy Transposable Elements Play Preferential Roles in Sex Chromosome Differentiation?Life (Basel). 2022 Apr 1;12(4):522. doi: 10.3390/life12040522. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35455013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lessons from an unusual vertebrate sex-determining gene.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2021 Aug 30;376(1832):20200092. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2020.0092. Epub 2021 Jul 12. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34247499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mobile Elements in Ray-Finned Fish Genomes.Life (Basel). 2020 Sep 25;10(10):221. doi: 10.3390/life10100221. Life (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32992841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic Instability of the Sex-Determining Locus in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar).G3 (Bethesda). 2015 Sep 22;5(11):2513-22. doi: 10.1534/g3.115.020115. G3 (Bethesda). 2015. PMID: 26401030 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bessereau JL. 2006. Transposon in C. elegans. In: WormBook: The Online Review of C. elegans Biology [Internet]. Pasadena (CA): WormBook; 2005-. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK19727/.
-
- Brunelli JP, Wertzler KJ, Sundin K, Thorgaard GH. 2008. Y-specific sequences and polymorphisms in rainbow trout and Chinook salmon. Genome 51:739–748. - PubMed
-
- Burke WD, Malik HS, Jones JP, Eickbush TH. 1999. The domain structure and retrotransposition mechanism of R2 elements are conserved throughout arthropods. Mol Biol Evol. 16(4):502–511. - PubMed
-
- Casacuberta JM, Santiago N. 2003. Plant LTR-retrotransposons and MITEs: control of transposition and impact on the evolution of plant genes and genomes. Gene 311:1–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

