Immediate Discharge and Home Treatment With Rivaroxaban of Low-risk Venous Thromboembolism Diagnosed in Two U.S. Emergency Departments: A One-year Preplanned Analysis
- PMID: 26113241
- PMCID: PMC5034796
- DOI: 10.1111/acem.12711
Immediate Discharge and Home Treatment With Rivaroxaban of Low-risk Venous Thromboembolism Diagnosed in Two U.S. Emergency Departments: A One-year Preplanned Analysis
Abstract
Objectives: The study hypothesis was that a target-specific anticoagulant would allow successful home treatment of selected patients with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) diagnosed in two urban emergency departments (EDs).
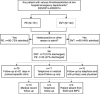
Methods: A protocol was established for treating low-risk DVT or PE patients with rivaroxaban and clinic, follow-up at both 2 to 5 weeks, and 3 to 6 months. Patients were determined to be low-risk by using a modified version of the Hestia criteria, supplemented by additional criteria for patients with active cancer. Acceptable outcome rates were defined as venous thromboembolism (VTE) recurrence ≤ 2.1% or bleeding ≤ 9.4% during treatment. VTE recurrence required positive imaging of any VTE. The International Society of Thrombosis and Hemostasis definition of major or clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding was used.
Results: From March 2013 through April 2014, a total of 106 patients were treated. Seventy-one (68%) had DVT, 30 (28%) had PE, and five (3%) had both, representing 51% of all DVTs and 27% of all PEs diagnosed in both EDs during the period of study. The 106 patients have been followed for a mean (±SD) of 389 (±111) days (range = 213 to 594 days). No patient had VTE recurrence, and no patient had a major or clinically relevant bleeding event while on therapy (none of the 106, 0%, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0% to 3.4%). However, three patients 2.8% (95% CI = 1% to 8%) had recurrent DVT after cessation of therapy.
Conclusions: Patients diagnosed with VTE and immediately discharged from the ED while treated with rivaroxaban had a low rate of VTE recurrence and bleeding.
© 2015 by the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine.
Figures
Comment in
-
Hot Off the Press: Outpatient Anticoagulation for Venous Thromboembolism Diagnosed in the Emergency Department.Acad Emerg Med. 2015 Nov;22(11):1355-7. doi: 10.1111/acem.12809. Epub 2015 Oct 15. Acad Emerg Med. 2015. PMID: 26469358 No abstract available.
References
-
- Vinson DR, Zehtabchi S, Yealy DM. Can selected patients with newly diagnosed pulmonary embolism be safely treated without hospitalization? A systematic review. Ann Emerg Med 2012;60:651–62. - PubMed
-
- Piran S, Le Gal G, Wells PS, et al. Outpatient treatment of symptomatic pulmonary embolism: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Thromb Res 2013;132:515–9. - PubMed
-
- Zondag W, Kooiman J, Klok FA, Dekkers OM, Huisman MV. Outpatient versus inpatient treatment in patients with pulmonary embolism: a meta‐analysis. Eur Respir J 2013;42:134–44. - PubMed
-
- Bauersachs R, Berkowitz SD, Brenner B, et al. Oral rivaroxaban for symptomatic venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med 2010;363:2499–510. - PubMed
-
- Buller HR, Prins MH, Lensin AW, et al. Oral rivaroxaban for the treatment of symptomatic pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med 2012;366:1287–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous