Effect of Matrine on HPAC cell migration by down-regulating the expression of MT1-MMP via Wnt signaling
- PMID: 26113801
- PMCID: PMC4480578
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-015-0210-4
Effect of Matrine on HPAC cell migration by down-regulating the expression of MT1-MMP via Wnt signaling
Abstract
Aim: This study sought to explore the exact mechanism of Matrine inhibited migration and invasion of human pancreatic cancer cells.
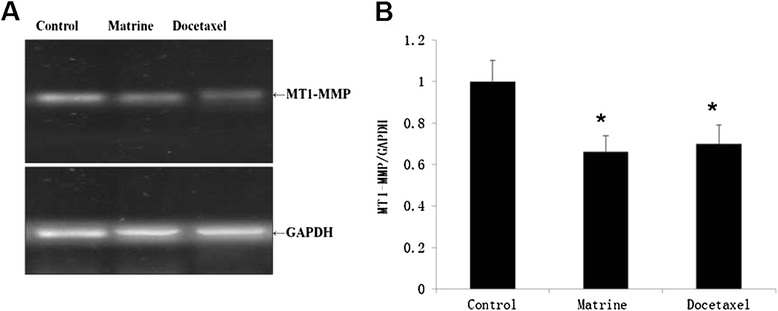
Methods: HPAC or Capan-1 cells were cultured in completed RPMI-1640 medium, contained with 50 μg/ml Matrine or 0.05 μg/ml docetaxel, respectively. Cell viability was evaluated by spectrophotometric analysis using MTT assay. Wound healing assay and transwell approach were used to detect the effects of Matrine on HPAC cell migration and invasion. Western Blot and RT-PCR were performed to detect the expressions of MT1-MMP, Wnt and β-Catenin. CHIP assay was used to detect whether the MT1-MMP transcription activity correlated with Wnt signaling pathway.
Results: MTT results indicated that cell proliferration was inhibited by Matrine at a range of concentrations, especially at high dose. We further found that Matrine treatment significantly induced cell migration and invasion decreased. Interestingly, the expression of MT1-MMP decreased evidently upon Matrine treatment, paralleled with the expressions of Wnt and β-Catenin detected by Western Blot and RT-PCR assay. Further analysis of MT1-MMP transcription activity revealed that Matrine reduced the expression of MT1-MMP mediated by Wnt signaling pathway.
Conclusion: Matrine play a vital role in inhibiting HPAC cellular migration and invasion through down-regulating the expression of MT1-MMP via Wnt signaling pathway.
Keywords: Cell migration; Human pancreatic cancer; MT1-MMP; Matrine; Wnt.
Figures



References
-
- Qiu S, Sun H, Zhang AH, Xu HY, Yan GL, Han Y, Wang XJ. Natural alkaloids: basic aspects, biological roles, and future perspectives. Chin J Nat Med. 2014;12(6):401–6. - PubMed
-
- Niu H, Zhang Y, Wu B, Zhang Y, Jiang H, He P. Matrine induces the apoptosis of lung cancer cells through downregulation of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins and the Akt signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 2014;32(3):1087–93. - PubMed
-
- Zhang JW, Su K, Shi WT, Wang Y, Hu PC, Wang Y, Wei L, Xiang J, Yang F. Matrine inhibits the adhesion and migration of BCG823 gastric cancer cells by affecting the structure and function of the vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013;34(8):1084–92. doi: 10.1038/aps.2013.15. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

