Estimating Gestational Age in Late Presenters to Antenatal Care in a Resource-Limited Setting on the Thai-Myanmar Border
- PMID: 26114295
- PMCID: PMC4482646
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131025
Estimating Gestational Age in Late Presenters to Antenatal Care in a Resource-Limited Setting on the Thai-Myanmar Border
Abstract
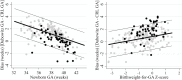
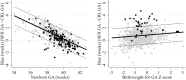
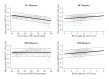
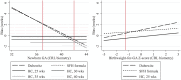
Estimating gestational age in resource-limited settings is prone to considerable inaccuracy because crown-rump length measured by ultrasound before 14 weeks gestation, the recommended method for estimating gestational age, is often unavailable. Judgements regarding provision of appropriate obstetric and neonatal care are dependent on accurate estimation of gestational age. We determined the accuracy of the Dubowitz Gestational Age Assessment, a population-specific symphysis-fundal height formula, and ultrasound biometry performed between 16 and 40 weeks gestation in estimating gestational age using pre-existing data from antenatal clinics of the Shoklo Malaria Research Unit on the Thai-Myanmar border, where malaria is endemic. Two cohorts of women who gave birth to live singletons were analysed: 1) 250 women who attended antenatal care between July 2001 and May 2006 and had both ultrasound crown-rump length (reference) and a Dubowitz Gestational Age Assessment; 2) 975 women attending antenatal care between April 2007 and October 2010 who had ultrasound crown-rump length, symphysis-fundal measurements, and an additional study ultrasound (biparietal diameter and head circumference) randomly scheduled between 16 and 40 weeks gestation. Mean difference in estimated newborn gestational age between methods and 95% limits of agreement (LOA) were determined from linear mixed-effects models. The Dubowitz method and the symphysis-fundal height formula performed well in term newborns, but overestimated gestational age of preterms by 2.57 weeks (95% LOA: 0.49, 4.65) and 3.94 weeks (95% LOA: 2.50, 5.38), respectively. Biparietal diameter overestimated gestational age by 0.83 weeks (95% LOA: -0.93, 2.58). Head circumference underestimated gestational age by 0.39 weeks (95% LOA: -2.60, 1.82), especially if measured after 24 weeks gestation. The results of this study can be used to quantify biases associated with alternative methods for estimating gestational age in the absence of ultrasound crown-rump length to inform critical clinical judgements in this population, and as a point of reference elsewhere.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Determination of gestational age after the 24th week of gestation from fetal kidney length measurements.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2002 Jun;19(6):592-7. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-0705.2002.00704.x. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2002. PMID: 12047540
-
Performance of late pregnancy biometry for gestational age dating in low-income and middle-income countries: a prospective, multicountry, population-based cohort study from the WHO Alliance for Maternal and Newborn Health Improvement (AMANHI) Study Group.Lancet Glob Health. 2020 Apr;8(4):e545-e554. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30034-6. Lancet Glob Health. 2020. PMID: 32199122 Free PMC article.
-
Biparietal diameter and crown-rump length in fetuses with Down's syndrome: implications for antenatal serum screening for Down's syndrome.Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1993 May;100(5):430-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1993.tb15267.x. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1993. PMID: 8518242
-
Nontraditional sonographic pearls in estimating gestational age.Semin Perinatol. 2008 Jun;32(3):154-60. doi: 10.1053/j.semperi.2008.02.003. Semin Perinatol. 2008. PMID: 18482614 Review.
-
[Role of ultrasound in elective abortions].J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2016 Dec;45(10):1477-1489. doi: 10.1016/j.jgyn.2016.09.032. Epub 2016 Nov 1. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2016. PMID: 27814980 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia in a Marginalized Population on the Thai-Myanmar Border: a study protocol.BMC Pediatr. 2017 Jan 21;17(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12887-017-0798-8. BMC Pediatr. 2017. PMID: 28109243 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the diagnostic accuracy of postnatal clinical scoring methods and foot length measurement for estimating gestational age and birthweight of newborns in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ Paediatr Open. 2024 Aug 30;8(1):e002717. doi: 10.1136/bmjpo-2024-002717. BMJ Paediatr Open. 2024. PMID: 39214548 Free PMC article.
-
Indirect neonatal hyperbilirubinemia in hospitalized neonates on the Thai-Myanmar border: a review of neonatal medical records from 2009 to 2014.BMC Pediatr. 2018 Jun 12;18(1):190. doi: 10.1186/s12887-018-1165-0. BMC Pediatr. 2018. PMID: 29895274 Free PMC article.
-
Extreme neonatal hyperbilirubinaemia in refugee and migrant populations: retrospective cohort.BMJ Paediatr Open. 2020 May 28;4(1):e000641. doi: 10.1136/bmjpo-2020-000641. eCollection 2020. BMJ Paediatr Open. 2020. PMID: 32537522 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal-foetal transfer of Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax antibodies in a low transmission setting.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 10;6:20859. doi: 10.1038/srep20859. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26861682 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

