Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Action of Sulfone Derivatives Containing 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Moieties on Rice Bacterial Leaf Blight
- PMID: 26114927
- PMCID: PMC6332022
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules200711660
Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Action of Sulfone Derivatives Containing 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Moieties on Rice Bacterial Leaf Blight
Abstract
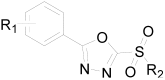
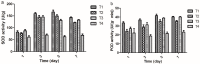
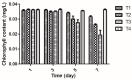
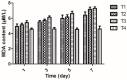
In this study, sulfone derivatives containing 1,3,4-oxadiazole moieties indicated good antibacterial activities against rice bacterial leaf blight caused by the pathogen Xanthomonas oryzaepv. pv. oryzae (Xoo). In particular, 2-(methylsulfonyl)-5-(4-fluorobenzyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole revealed the best antibacterial activity against Xoo, with a half-maximal effective concentration (EC50) of 9.89 μg/mL, which was better than those of the commercial agents of bismerthiazole (92.61 μg/mL) and thiodiazole copper (121.82 μg/mL). In vivo antibacterial activity tests under greenhouse conditions and field trials demonstrated that 2-(methylsulfonyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole was effective in reducing rice bacterial leaf blight. Meanwhile, 2-(methylsulfonyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole stimulate the increase in superoxide dismutase (SOD) and peroxidase (POD) activities in rice, causing marked enhancement of plant resistance against rice bacterial leaf blight. It could also improve the chlorophyll content and restrain the increase in the malondialdehyde (MDA) content in rice to considerably reduce the amount of damage caused by Xoo. Moreover, 2-(methylsulfonyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole, at a concentration of 20 μg/mL, could inhibit the production of extracellular polysaccharide (EPS) with an inhibition ratio of 94.52%, and reduce the gene expression levels of gumB, gumG, gumM, and xanA, with inhibition ratios of 94.88%, 68.14%, 86.76%, and 79.21%, respectively.
Keywords: Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae; action mechanism; antibacterial activity; extracellular polysaccharide; sulfone derivative.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
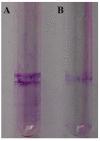

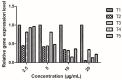
Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis, and antibacterial activity against rice bacterial leaf blight and leaf streak of 2,5-substituted-1,3,4-oxadiazole/thiadiazole sulfone derivative.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014 Apr 1;24(7):1677-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.02.060. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014. PMID: 24631191
-
Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of New Sulfone Derivatives Containing a 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Moiety as Active Antibacterial Agents.J Agric Food Chem. 2018 Mar 28;66(12):3093-3100. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b06061. Epub 2018 Mar 9. J Agric Food Chem. 2018. PMID: 29502398
-
Antibacterial activities against rice bacterial leaf blight and tomato bacterial wilt of 2-mercapto-5-substituted-1,3,4-oxadiazole/thiadiazole derivatives.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015 Feb 1;25(3):481-4. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.12.038. Epub 2014 Dec 19. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015. PMID: 25563889
-
Rice Routes of Countering Xanthomonas oryzae.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 2;19(10):3008. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103008. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30279356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of the Biological Activities of Heterocyclic Compounds Comprising Oxadiazole Moieties.Curr Top Med Chem. 2022;22(7):578-599. doi: 10.2174/1568026622666220202123651. Curr Top Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35114924 Review.
Cited by
-
SstF, a novel sulforaphane-sensing transcription factor of Xanthomonas campestris, is required for sulforaphane tolerance and virulence.Mol Plant Pathol. 2023 May;24(5):452-465. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13314. Epub 2023 Feb 24. Mol Plant Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36829260 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of Ethyl 2-Nitro-3-Arylacrylates Molecules as T3SS Inhibitor Reducing the Virulence of Plant Pathogenic Bacteria Xanthomonas.Front Microbiol. 2019 Aug 20;10:1874. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01874. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31481941 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial and biofilm inhibition activity of biofabricated silver nanoparticles against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae causing blight disease of rice instigates disease suppression.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Mar 16;36(4):55. doi: 10.1007/s11274-020-02826-1. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32180020
-
Antibacterial activities of coumarin-3-carboxylic acid against Acidovorax citrulli.Front Microbiol. 2023 Sep 20;14:1207125. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1207125. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37799610 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship study of quinazoline derivatives containing a 1,3,4-oxadiazole moiety as efficient inhibitors against Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri.Mol Divers. 2018 Nov;22(4):791-802. doi: 10.1007/s11030-018-9837-0. Epub 2018 May 28. Mol Divers. 2018. PMID: 29808346
References
-
- Mew T.W. Current status and future prospects of research on bacterial blight of rice. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1987;25:359–382. doi: 10.1146/annurev.py.25.090187.002043. - DOI
-
- Nayak D., Shanti M.L., Bose L.K., Singh U.D., Nayak P. Pathogenicity association in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae the causal organism of rice bacterial blight disease. ARPN J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2008;3:12–26.
-
- Shanti M.L., Devi G.L., Kumar G.N., Shashidhar H.E. Molecular marker-assisted selection: A tool for insulating parental lines of hybrid rice against bacterial leaf blight. Int. J. Plant Pathol. 2010;1:114–123. doi: 10.3923/ijpp.2010.114.123. - DOI
-
- Evidente A., Venturi V., Masi M., Degrassi G., Cimmino A., Maddau L., Andolfi A. In vitro antibacterial activity of sphaeropsidins and chemical derivatives toward Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, the causal agent of rice bacterial blight. J. Nat. Prod. 2011;74:2520–2525. doi: 10.1021/np200625m. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Khoshkdaman M., Ebadi A.A., Kahrizi D. Evaluation of pathogencity and race classification of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in guilan province-Iran. Agric. Sci. 2012;3:557–561.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

