Pathways to Drinking Among Hispanic/Latino Adolescents: Perceived Discrimination, Ethnic Identity, and Peer Affiliations
- PMID: 26115004
- PMCID: PMC9423721
- DOI: 10.1080/15332640.2014.993787
Pathways to Drinking Among Hispanic/Latino Adolescents: Perceived Discrimination, Ethnic Identity, and Peer Affiliations
Abstract
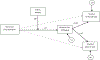
We examined whether discrimination experienced by Hispanic/Latino adolescents is associated (a) directly with adolescent alcohol use or (b) indirectly with adolescent alcohol use via mediation by ethnic identity and/or peer associations. Data were drawn from an NIAAA-funded randomized controlled trial evaluating the efficacy of a Guided-Self Change intervention for Hispanic/Latino youth with alcohol and interpersonal violence problems (R01 AA12180; see Wagner et al., 2014). The current sample included 371 Hispanic/Latino teenagers (mean age = 16.3 years [SD = 1.37]; 38% female). Using structural equation modeling (SEM), results revealed that perceived discrimination was indirectly related to alcohol consumption through positive (non-drinking) peer affiliations. Additionally, ethnic identity was found to moderate the relationship between discrimination and positive peer affiliation. These findings further our understanding about how discrimination and ethnic identity interact, as well as provide directions for how the effectiveness of prevention models may be enhanced for reducing underage drinking among Hispanic/Latino adolescents.
Keywords: Hispanic/Latino; adolescents; alcohol use; ethnic identity; peers.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Trajectories of perceived adult and peer discrimination among Black, Latino, and Asian American adolescents: patterns and psychological correlates.Dev Psychol. 2006 Mar;42(2):218-36. doi: 10.1037/0012-1649.42.2.218. Dev Psychol. 2006. PMID: 16569162
-
Examination of the indirect effect of alcohol expectancies on ethnic identity and adolescent drinking outcomes.Am J Orthopsychiatry. 2019;89(5):600-608. doi: 10.1037/ort0000390. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Am J Orthopsychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30688482 Free PMC article.
-
The mediation process between Latino youths' family ethnic socialization, ethnic-racial identity, and academic engagement: Moderation by ethnic-racial discrimination?Cultur Divers Ethnic Minor Psychol. 2021 Apr;27(2):296-306. doi: 10.1037/cdp0000349. Epub 2020 May 14. Cultur Divers Ethnic Minor Psychol. 2021. PMID: 32406701
-
Ethnicity and image: correlates of crowd affiliation among ethnic minority youth.Child Dev. 2008 May-Jun;79(3):529-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8624.2008.01141.x. Child Dev. 2008. PMID: 18489411
-
The Role of Ethnicity and Culture in Adolescent Health in Latine, Hispanic, and Spanish Populations.Prim Care. 2024 Dec;51(4):581-589. doi: 10.1016/j.pop.2024.05.002. Epub 2024 Jun 12. Prim Care. 2024. PMID: 39448095 Review.
Cited by
-
Perceived Discrimination and Substance Use among Adolescents: Examining the Moderating Effect of Distress Tolerance and Negative Urgency.Subst Use Misuse. 2019;54(1):156-165. doi: 10.1080/10826084.2018.1512625. Epub 2018 Nov 5. Subst Use Misuse. 2019. PMID: 30395759 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term impact of familismo and ethnic identity on latinx college student drinking and high-risk consequences.J Ethn Subst Abuse. 2024 Apr-Jun;23(2):201-221. doi: 10.1080/15332640.2022.2082618. Epub 2022 Jun 4. J Ethn Subst Abuse. 2024. PMID: 38768079 Free PMC article.
-
Racism-related experiences and substance use: A systematic and meta-analytic review.Soc Sci Med. 2024 Dec;362:117434. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2024.117434. Epub 2024 Oct 21. Soc Sci Med. 2024. PMID: 39461166
-
How Ethnic Minority Context Alters the Risk for Developing Mental Health Disorders and Psychological Distress for Latinx Young Adults.Milbank Q. 2022 Jun;100(2):424-463. doi: 10.1111/1468-0009.12552. Epub 2022 Feb 21. Milbank Q. 2022. PMID: 35191095 Free PMC article.
-
Intragroup xenophobic attitudes, ethnic identity, and substance use among Latinx adolescents.J Ethn Subst Abuse. 2020 Jul-Sep;19(3):417-434. doi: 10.1080/15332640.2018.1540954. Epub 2019 Jan 12. J Ethn Subst Abuse. 2020. PMID: 30636571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Austin GA, & Gilbert MJ (1989). Substance Use among Latino Youth. Prevention Research Update, 3, 1–28.
-
- Bacallao ML, Smokowski PR (2009).Obstacles to Getting Ahead: How Assimilation Mechanisms Impact Mexican Immigrant Families. Journal of Health and Social Policy. - PubMed
-
- Berry JW (1997). Immigration, acculturation, and adaptation. Applied psychology, 46(1), 5–34.
-
- Bollen KA & Stine R (1993). Bootstrapping goodness of fit measures in structural equation models. In: Bollen KA, Long JS (Eds.), Testing Structural Equation Models, Sage, Newbury Park, CA. pp. 111–135.
-
- Breslin C, Li S, Sdao-Jarvie K, Tupker E, & Ittig-Deland V (2002). Brief treatment for young substance abusers: a pilot study in an addiction treatment setting. Psychology of Addictive behaviors, 16(1), 10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
