Injecting risk behaviours following treatment for hepatitis C virus infection among people who inject drugs: The Australian Trial in Acute Hepatitis C
- PMID: 26115881
- PMCID: PMC4577441
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drugpo.2015.05.003
Injecting risk behaviours following treatment for hepatitis C virus infection among people who inject drugs: The Australian Trial in Acute Hepatitis C
Abstract
Background: A barrier to hepatitis C virus (HCV) treatment among people who inject drugs (PWID) has been a concern that interferon-based HCV treatment may increase injecting risk behaviours. This study evaluated recent (past month) injecting risk behaviours during follow-up among PWID that did and did not receive HCV treatment.
Methods: The Australian Trial in Acute Hepatitis C (ATAHC) was a prospective study of natural history and treatment of recent HCV infection. Analyses were performed using generalized estimating equations.
Results: Among 124 participants with a history of injecting drug use (median age 32 years), 69% were male, and 68% were treated for HCV infection. HCV treatment was not associated with an increase in recent injecting drug use (adjusted odds ratio (aOR) 1.06, 95% CI 0.93, 1.21) or recent used needle and syringe borrowing during follow-up (aOR 0.99, 95% CI 0.89, 1.08). HCV treatment was associated with a decrease in recent ancillary injecting equipment sharing during follow-up (aOR 0.85, 95% CI 0.74, 0.99). Further, among treated participants who remained in follow-up (n=24), ancillary injecting equipment sharing significantly decreased from 54% at enrolment to 17% during follow-up (P=0.012).
Conclusions: HCV treatment was not associated with drug use or used needle and syringe borrowing during follow-up, but was associated with decreased ancillary injecting equipment sharing during follow-up. Programs to enhance HCV assessment and treatment among PWID should be expanded, given that HCV treatment does not lead to increases in injecting risk behaviours and has previously been demonstrated to be safe and effective among PWID.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00192569.
Keywords: Antiviral therapy; HCV; Injecting drug use; People who inject drugs.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The other authors who have taken part in this study declared that they do not have anything to disclose regarding funding or conflict of interest with respect to this manuscript.
Figures

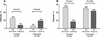
References
-
- Hajarizadeh B, Grebely J, Dore GJ. Epidemiology and natural history of HCV infection. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology Hepatology. 2013;10(9):553–562. - PubMed
-
- Dore GJ, Grebely J. What is killing people with hepatitis C virus infection? Seminars in Liver Disease. 2011;31(4):331–339. - PubMed
-
- Grebely J, Dore GJ. Can hepatitis C virus infection be eradicated in people who inject drugs? Antiviral research. 2014;104:62–72. - PubMed
-
- Hellard M, Sacks-Davis R, Gold J. Hepatitis C treatment for injection drug users: a review of the available evidence. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2009;49(4):561–573. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

