Pioglitazone in early Parkinson's disease: a phase 2, multicentre, double-blind, randomised trial
- PMID: 26116315
- PMCID: PMC4574625
- DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(15)00144-1
Pioglitazone in early Parkinson's disease: a phase 2, multicentre, double-blind, randomised trial
Erratum in
- Lancet Neurol. 2015 Oct; 14(10):979
Abstract
Background: A systematic assessment of potential disease-modifying compounds for Parkinson's disease concluded that pioglitazone could hold promise for the treatment of patients with this disease. We assessed the effect of pioglitazone on the progression of Parkinson's disease in a multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled, futility clinical trial.
Methods: Participants with the diagnosis of early Parkinson's disease on a stable regimen of 1 mg/day rasagiline or 10 mg/day selegiline were randomly assigned (1:1:1) to 15 mg/day pioglitazone, 45 mg/day pioglitazone, or placebo. Investigators were masked to the treatment assignment. Only the statistical centre and the central pharmacy knew the treatment name associated with the randomisation number. The primary outcome was the change in the total Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) score between the baseline and 44 weeks, analysed by intention to treat. The primary null hypothesis for each dose group was that the mean change in UPDRS was 3 points less than the mean change in the placebo group. The alternative hypothesis (of futility) was that pioglitazone is not meaningfully different from placebo. We rejected the null if there was significant evidence of futility at the one-sided alpha level of 0·10. The study is registered at ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT01280123.
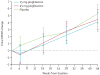
Findings: 210 patients from 35 sites in the USA were enrolled between May 10, 2011, and July 31, 2013. The primary analysis included 72 patients in the 15 mg group, 67 in the 45 mg group, and 71 in the placebo group. The mean total UPDRS change at 44 weeks was 4·42 (95% CI 2·55-6·28) for 15 mg pioglitazone, 5·13 (95% CI 3·17-7·08) for 45 mg pioglitazone, and 6·25 (95% CI 4·35-8·15) for placebo (higher change scores are worse). The mean difference between the 15 mg and placebo groups was -1·83 (80% CI -3·56 to -0·10) and the null hypothesis could not be rejected (p=0·19). The mean difference between the 45 mg and placebo groups was -1·12 (80% CI -2·93 to 0·69) and the null hypothesis was rejected in favour of futility (p=0·09). Planned sensitivity analyses of the primary outcome, using last value carried forward (LVCF) to handle missing data and using the completers' only sample, suggested that the 15 mg dose is also futile (p=0·09 for LVCF, p=0·09 for completers) but failed to reject the null hypothesis for the 45 mg dose (p=0·12 for LVCF, p=0·19 for completers). Six serious adverse events occurred in the 15 mg group, nine in the 45 mg group, and three in the placebo group; none were thought to be definitely or probably related to the study interventions.
Interpretation: These findings suggest that pioglitazone at the doses studied here is unlikely to modify progression in early Parkinson's disease. Further study of pioglitazone in a larger trial in patients with Parkinson's disease is not recommended.
Funding: National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Neuroprotection in Parkinson's disease: a difficult challenge.Lancet Neurol. 2015 Aug;14(8):780-781. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(15)00143-X. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Lancet Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26116314 No abstract available.
-
Parkinson disease: Laying the foundations for disease-modifying therapies in PD.Nat Rev Neurol. 2015 Oct;11(10):553-5. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2015.150. Epub 2015 Aug 25. Nat Rev Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26303855
References
-
- de Lau LM, Breteler MM. Epidemiology of Parkinson's disease. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5:525–35. - PubMed
-
- Suchowersky O, Gronseth G, Perlmutter J, Reich S, Zesiewicz T, Weiner WJ. Practice parameter: neuroprotective strategies and alternative therapies for Parkinson disease (an evidence-based review): report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology. 2006;66:976–82. - PubMed
-
- Hart RG, Pearce LA, Ravina BM, Yaltho TC, Marler JR. Neuroprotection trials in Parkinson's disease: systematic review. Mov Disord. 2009;24:647–54. - PubMed
-
- Ravina BM, Fagan SC, Hart RG, et al. Neuroprotective agents for clinical trials in Parkinson's disease: a systematic assessment. Neurology. 2003;60:1234–40. - PubMed
-
- Chaturvedi RK, Beal MF. PPAR: a therapeutic target in Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem. 2008;106:506–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

