Mitochondrial Dihydrolipoyl Dehydrogenase Activity Shapes Photosynthesis and Photorespiration of Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 26116608
- PMCID: PMC4531348
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.15.00105
Mitochondrial Dihydrolipoyl Dehydrogenase Activity Shapes Photosynthesis and Photorespiration of Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
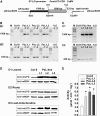
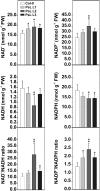
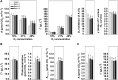
Mitochondrial dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase (mtLPD; L-protein) is an integral component of several multienzyme systems involved in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, photorespiration, and the degradation of branched-chain α-ketoacids. The majority of the mtLPD present in photosynthesizing tissue is used for glycine decarboxylase (GDC), necessary for the high-flux photorespiratory glycine-into-serine conversion. We previously suggested that GDC activity could be a signal in a regulatory network that adjusts carbon flux through the Calvin-Benson cycle in response to photorespiration. Here, we show that elevated GDC L-protein activity significantly alters several diagnostic parameters of cellular metabolism and leaf gas exchange in Arabidopsis thaliana. Overexpressor lines displayed markedly decreased steady state contents of TCA cycle and photorespiratory intermediates as well as elevated NAD(P)(+)-to-NAD(P)H ratios. Additionally, increased rates of CO2 assimilation, photorespiration, and plant growth were observed. Intriguingly, however, day respiration rates remained unaffected. By contrast, respiration was enhanced in the first half of the dark phase but depressed in the second. We also observed enhanced sucrose biosynthesis in the light in combination with a lower diel magnitude of starch accumulation and breakdown. These data thus substantiate our prior hypothesis that facilitating flux through the photorespiratory pathway stimulates photosynthetic CO2 assimilation in the Calvin-Benson cycle. They furthermore suggest that this regulation is, at least in part, dependent on increased light-capture/use efficiency.
© 2015 American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Aliyev J.A. (2012). Photosynthesis, photorespiration and productivity of wheat and soybean genotypes. Physiol. Plant. 145: 369–383. - PubMed
-
- Anderson L.E. (1971). Chloroplast and cytoplasmic enzymes. II. Pea leaf triose phosphate isomerases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 235: 237–244. - PubMed
-
- Andrews T.J., Lorimer G.H., Tolbert N.E. (1973). Ribulose diphosphate oxygenase. I. Synthesis of phosphoglycolate by fraction-1 protein of leaves. Biochemistry 12: 11–18. - PubMed
-
- Araújo W.L., Ishizaki K., Nunes-Nesi A., Larson T.R., Tohge T., Krahnert I., Witt S., Obata T., Schauer N., Graham I.A., Leaver C.J., Fernie A.R. (2010). Identification of the 2-hydroxyglutarate and isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenases as alternative electron donors linking lysine catabolism to the electron transport chain of Arabidopsis mitochondria. Plant Cell 22: 1549–1563. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Araújo W.L., Tohge T., Osorio S., Lohse M., Balbo I., Krahnert I., Sienkiewicz-Porzucek A., Usadel B., Nunes-Nesi A., Fernie A.R. (2012). Antisense inhibition of the 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex in tomato demonstrates its importance for plant respiration and during leaf senescence and fruit maturation. Plant Cell 24: 2328–2351. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

