Effects of Exercise Training on Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Biomarkers of Cardiometabolic Health: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 26116691
- PMCID: PMC4608087
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.115.002014
Effects of Exercise Training on Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Biomarkers of Cardiometabolic Health: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
Background: Guidelines recommend exercise for cardiovascular health, although evidence from trials linking exercise to cardiovascular health through intermediate biomarkers remains inconsistent. We performed a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials to quantify the impact of exercise on cardiorespiratory fitness and a variety of conventional and novel cardiometabolic biomarkers in adults without cardiovascular disease.
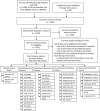
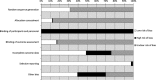
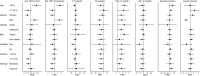
Methods and results: Two researchers selected 160 randomized controlled trials (7487 participants) based on literature searches of Medline, Embase, and Cochrane Central (January 1965 to March 2014). Data were extracted using a standardized protocol. A random-effects meta-analysis and systematic review was conducted to evaluate the effects of exercise interventions on cardiorespiratory fitness and circulating biomarkers. Exercise significantly raised absolute and relative cardiorespiratory fitness. Lipid profiles were improved in exercise groups, with lower levels of triglycerides and higher levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and apolipoprotein A1. Lower levels of fasting insulin, homeostatic model assessment-insulin resistance, and glycosylated hemoglobin A1c were found in exercise groups. Compared with controls, exercise groups had higher levels of interleukin-18 and lower levels of leptin, fibrinogen, and angiotensin II. In addition, we found that the exercise effects were modified by age, sex, and health status such that people aged <50 years, men, and people with type 2 diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, or metabolic syndrome appeared to benefit more.
Conclusions: This meta-analysis showed that exercise significantly improved cardiorespiratory fitness and some cardiometabolic biomarkers. The effects of exercise were modified by age, sex, and health status. Findings from this study have significant implications for future design of targeted lifestyle interventions.
Keywords: biomarker; cardiometabolic health; cardiovascular disease prevention; exercise training.
© 2015 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures

References
-
- Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Blaha MJ, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Franco S, Fullerton HJ, Gillespie C, Hailpern SM, Heit JA, Howard VJ, Huffman MD, Judd SE, Kissela BM, Kittner SJ, Lackland DT, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Mackey RH, Magid DJ, Marcus GM, Marelli A, Matchar DB, McGuire DK, Mohler ER, III, Moy CS, Mussolino ME, Neumar RW, Nichol G, Pandey DK, Paynter NP, Reeves MJ, Sorlie PD, Stein J, Towfighi A, Turan TN, Virani SS, Wong ND, Woo D, Turner MB. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2014 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2014;129:e28–e292. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lackland DT, Roccella EJ, Deutsch AF, Fornage M, George MG, Howard G, Kissela BM, Kittner SJ, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Schwamm LH, Smith EE, Towfighi A. Factors influencing the decline in stroke mortality: a statement from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2014;45:315–353. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pearson TA, Blair SN, Daniels SR, Eckel RH, Fair JM, Fortmann SP, Franklin BA, Goldstein LB, Greenland P, Grundy SM, Hong Y, Miller NH, Lauer RM, Ockene IS, Sacco RL, Sallis JF, Jr, Smith SC, Jr, Stone NJ, Taubert KA. AHA guidelines for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and stroke: 2002 update: consensus panel guide to comprehensive risk reduction for adult patients without coronary or other atherosclerotic vascular diseases. American Heart Association Science Advisory and Coordinating Committee. Circulation. 2002;106:388–391. - PubMed

