The α1A-adrenergic receptor subtype mediates increased contraction of failing right ventricular myocardium
- PMID: 26116709
- PMCID: PMC4591405
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00042.2015
The α1A-adrenergic receptor subtype mediates increased contraction of failing right ventricular myocardium
Abstract
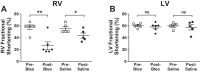
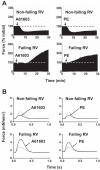
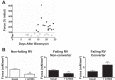
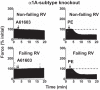
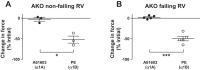
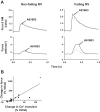
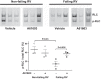
Dysfunction of the right ventricle (RV) is closely related to prognosis for patients with RV failure. Therefore, strategies to improve failing RV function are significant. In a mouse RV failure model, we previously reported that α1-adrenergic receptor (α1-AR) inotropic responses are increased. The present study determined the roles of both predominant cardiac α1-AR subtypes (α1A and α1B) in upregulated inotropy in failing RV. We used the mouse model of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension, and RV failure. We assessed the myocardial contractile response in vitro to stimulation of the α1A-subtype (using α1A-subtype-selective agonist A61603) and α1B-subtype [using α1A-subtype knockout mice and nonsubtype selective α1-AR agonist phenylephrine (PE)]. In wild-type nonfailing RV, a negative inotropic effect of α1-AR stimulation with PE (force decreased ≈50%) was switched to a positive inotropic effect (PIE) with bleomycin-induced RV injury. Upregulated inotropy in failing RV occurred with α1A-subtype stimulation (force increased ≈200%), but not with α1B-subtype stimulation (force decreased ≈50%). Upregulated inotropy mediated by the α1A-subtype involved increased activator Ca(2+) transients and increased phosphorylation of myosin regulatory light chain (a mediator of increased myofilament Ca(2+) sensitivity). In failing RV, the PIE elicited by the α1A-subtype was appreciably less when the α1A-subtype was stimulated in combination with the α1B-subtype, suggesting functional antagonism between α1A- and α1B-subtypes. In conclusion, upregulation of α1-AR inotropy in failing RV myocardium requires the α1A-subtype and is opposed by the α1B-subtype. The α1A subtype might be a therapeutic target to improve the function of the failing RV.
Keywords: inotropic; myosin regulatory light chain; right ventricle; α1-adrenergic.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

References
-
- ALLHAT Officers and Coordinators for the ALLHAT Collaborative Research Group. Major cardiovascular events in hypertensive patients randomized to doxazosin vs chlorthalidone: the antihypertensive, and lipid-lowering treatment to prevent heart attack trial (ALLHAT). JAMA 283: 1967–1975, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Andersen GG, Qvigstad E, Schiander I, Aass H, Osnes JB, Skomedal T. α1-AR-induced positive inotropic response in heart is dependent on myosin light chain phosphorylation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 283: H1471–H1480, 2002. - PubMed
-
- Baker AJ. Adrenergic signaling in heart failure: a balance of toxic and protective effects. Pflügers Arch 466: 1139–1150, 2014. - PubMed
-
- Brodde OE, Michel MC. Adrenergic and muscarinic receptors in the human heart. Pharmacol Rev 51: 651–690, 1999. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

