p62 links autophagy and Nrf2 signaling
- PMID: 26117325
- PMCID: PMC4628872
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.06.014
p62 links autophagy and Nrf2 signaling
Abstract
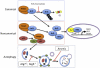
The Nrf2-Keap1-ARE pathway is a redox and xenobiotic sensitive signaling axis that functions to protect cells against oxidative stress, environmental toxicants, and harmful chemicals through the induction of cytoprotective genes. To enforce strict regulation, cells invest a great deal of energy into the maintenance of the Nrf2 pathway to ensure rapid induction upon cellular insult and rapid return to basal levels once the insult is mitigated. Because of the protective role of Nrf2 transcriptional programs, controlled activation of the pathway has been recognized as a means for chemoprevention. On the other hand, constitutive activation of Nrf2, due to somatic mutations of genes that control Nrf2 degradation, promotes carcinogenesis and imparts chemoresistance to cancer cells. Autophagy, a bulk protein degradation process, is another tightly regulated complex cellular process that functions as a cellular quality control system to remove damaged proteins or organelles. Low cellular nutrient levels can also activate autophagy, which acts to restore metabolic homeostasis through the degradation of macromolecules to provide nutrients. Recently, these two cellular pathways were shown to intersect through the direct interaction between p62 (an autophagy adaptor protein) and Keap1 (the Nrf2 substrate adaptor for the Cul3 E3 ubiquitin ligase). Dysregulation of autophagy was shown to result in prolonged Nrf2 activation in a p62-dependent manner. In this review, we will discuss the progress that has been made in dissecting the intersection of these two pathways and the potential tumor-promoting role of prolonged Nrf2 activation.
Copyright © 2015. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Itoh K, Ishii T, Wakabayashi N, Yamamoto M. Regulatory mechanisms of cellular response to oxidative stress. Free Radic Res. 1999;31:319–324. - PubMed
-
- Dinkova-Kostova AT, Holtzclaw WD, Cole RN, Itoh K, Wakabayashi N, Katoh Y, Yamamoto M, Talalay P. Direct evidence that sulfhydryl groups of Keap1 are the sensors regulating induction of phase 2 enzymes that protect against carcinogens and oxidants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:11908–11913. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

