The Mitochondrial Calcium Uniporter Selectively Matches Metabolic Output to Acute Contractile Stress in the Heart
- PMID: 26119742
- PMCID: PMC4497842
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.06.002
The Mitochondrial Calcium Uniporter Selectively Matches Metabolic Output to Acute Contractile Stress in the Heart
Abstract
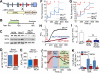
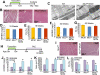
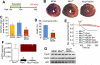
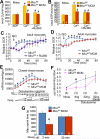
In the heart, augmented Ca(2+) fluxing drives contractility and ATP generation through mitochondrial Ca(2+) loading. Pathologic mitochondrial Ca(2+) overload with ischemic injury triggers mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP) opening and cardiomyocyte death. Mitochondrial Ca(2+) uptake is primarily mediated by the mitochondrial Ca(2+) uniporter (MCU). Here, we generated mice with adult and cardiomyocyte-specific deletion of Mcu, which produced mitochondria refractory to acute Ca(2+) uptake, with impaired ATP production, and inhibited MPTP opening upon acute Ca(2+) challenge. Mice lacking Mcu in the adult heart were also protected from acute ischemia-reperfusion injury. However, resting/basal mitochondrial Ca(2+) levels were normal in hearts of Mcu-deleted mice, and mitochondria lacking MCU eventually loaded with Ca(2+) after stress stimulation. Indeed, Mcu-deleted mice were unable to immediately sprint on a treadmill unless warmed up for 30 min. Hence, MCU is a dedicated regulator of short-term mitochondrial Ca(2+) loading underlying a "fight-or-flight" response that acutely matches cardiac workload with ATP production.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Beutner G, Sharma VK, Giovannucci DR, Yule DI, Sheu SS. Identification of a ryanodine receptor in rat heart mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:21482–21488. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R00 HL119353/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL080101/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL069779/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL108806/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL062927/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL030077/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- K99 HL119353/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL081104/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL060562/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL060562/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL095077/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

