Dynamic aberrant NF-κB spurs tumorigenesis: a new model encompassing the microenvironment
- PMID: 26119834
- PMCID: PMC4526340
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2015.06.001
Dynamic aberrant NF-κB spurs tumorigenesis: a new model encompassing the microenvironment
Abstract
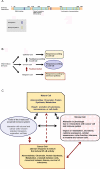
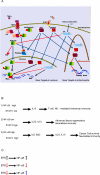
Recently it was discovered that a transient activation of transcription factor NF-κB can give cells properties essential for invasiveness and cancer initiating potential. In contrast, most oncogenes to date were characterized on the basis of mutations or by their constitutive overexpression. Study of NF-κB actually leads to a far more dynamic perspective on cancer: tumors caused by diverse oncogenes apparently evolve into cancer after loss of feedback regulation for NF-κB. This event alters the cellular phenotype and the expression of hormonal mediators, modifying signals between diverse cell types in a tissue. The result is a disruption of stem cell hierarchy in the tissue, and pervasive changes in the microenvironment and immune response to the malignant cells.
Keywords: Cancer; Homeostasis; Immunity; Inflammation; Nuclear Factor kappa B.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Lin D-C, Zhang Y, Pan Q-J, Yang H, et al. PLK1 Is transcriptionally activated by NF-κB during cell detachment and enhances anoikis resistance through inhibiting β-catenin degradation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2011;17:4285–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

