Broad Anti-tumor Activity of a Small Molecule that Selectively Targets the Warburg Effect and Lipogenesis
- PMID: 26120082
- PMCID: PMC4965273
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2015.05.007
Broad Anti-tumor Activity of a Small Molecule that Selectively Targets the Warburg Effect and Lipogenesis
Abstract
Malignant cells exhibit aerobic glycolysis (the Warburg effect) and become dependent on de novo lipogenesis, which sustains rapid proliferation and resistance to cellular stress. The nuclear receptor liver-X-receptor (LXR) directly regulates expression of key glycolytic and lipogenic genes. To disrupt these oncogenic metabolism pathways, we designed an LXR inverse agonist SR9243 that induces LXR-corepressor interaction. In cancer cells, SR9243 significantly inhibited the Warburg effect and lipogenesis by reducing glycolytic and lipogenic gene expression. SR9243 induced apoptosis in tumors without inducing weight loss, hepatotoxicity, or inflammation. Our results suggest that LXR inverse agonists may be an effective cancer treatment approach.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
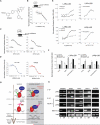

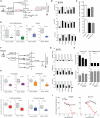
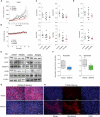
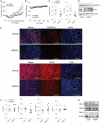

Comment in
-
Are Synthetic Compounds that Silence the Liver-X-Receptor the Next Generation of Anti-cancer Drugs?Cancer Cell. 2015 Jul 13;28(1):3-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2015.06.013. Cancer Cell. 2015. PMID: 26175408
-
Anticancer drugs: Repressing LXRs to starve cancer.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015 Sep;14(9):602. doi: 10.1038/nrd4714. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015. PMID: 26323542 No abstract available.
References
-
- Baranowski M. Biological role of liver X receptors. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2008;59(Suppl 7):31–55. - PubMed
-
- Beyea MM, Heslop CL, Sawyez CG, Edwards JY, Markle JG, Hegele RA, Huff MW. Selective up-regulation of LXR-regulated genes ABCA1, ABCG1, and APOE in macrophages through increased endogenous synthesis of 24(S),25-epoxycholesterol. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282:5207–5216. - PubMed
-
- Blancher C, Harris AL. The molecular basis of the hypoxia response pathway: tumour hypoxia as a therapy target. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1998;17:187–194. - PubMed
-
- Bonuccelli G, Tsirigos A, Whitaker-Menezes D, Pavlides S, Pestell RG, Chiavarina B, Frank PG, Flomenberg N, Howell A, Martinez-Outschoorn UE, et al. Ketones and lactate “fuel” tumor growth and metastasis: Evidence that epithelial cancer cells use oxidative mitochondrial metabolism. Cell Cycle. 2010;9:3506–3514. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

