Diffuse Optics for Tissue Monitoring and Tomography
- PMID: 26120204
- PMCID: PMC4482362
- DOI: 10.1088/0034-4885/73/7/076701
Diffuse Optics for Tissue Monitoring and Tomography
Abstract
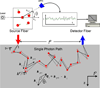
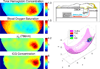
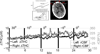
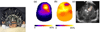
This review describes the diffusion model for light transport in tissues and the medical applications of diffuse light. Diffuse optics is particularly useful for measurement of tissue hemodynamics, wherein quantitative assessment of oxy- and deoxy-hemoglobin concentrations and blood flow are desired. The theoretical basis for near-infrared or diffuse optical spectroscopy (NIRS or DOS, respectively) is developed, and the basic elements of diffuse optical tomography (DOT) are outlined. We also discuss diffuse correlation spectroscopy (DCS), a technique whereby temporal correlation functions of diffusing light are transported through tissue and are used to measure blood flow. Essential instrumentation is described, and representative brain and breast functional imaging and monitoring results illustrate the workings of these new tissue diagnostics.
Figures












References
-
- Cutler M. Transillumination of the breast. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1929;48:721–727.
-
- Jobsis FF. Noninvasive infrared monitoring of cerebral and myocardial sufficiency and circulatory parameters. Science. 1977;198:1264–1267. - PubMed
-
- Jobsis-vanderVliet FF, Jobsis PD. Biochemical and physiological basis of medical near-infrared spectroscopy. Journal of Biomedical Optics. 1999;4:397. - PubMed
-
- Jöbsis-vanderVliet FF. Discovery of the near-infrared window into the body and the early development of near-infrared spectroscopy. Journal of Biomedical Optics. 1999;4:392. - PubMed
-
- Yodh A, Chance B. Spectroscopy and imaging with diffusing light. Physics Today. 1995;48(3):34–40.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
