The molecular ticks of the Drosophila circadian clock
- PMID: 26120561
- PMCID: PMC4480617
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cois.2015.01.002
The molecular ticks of the Drosophila circadian clock
Abstract
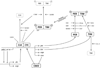
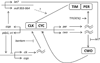
Drosophila is a powerful model to understand the mechanisms underlying circadian rhythms. The Drosophila molecular clock is comprised of transcriptional feedback loops. The expressions of the critical transcriptional activator CLK and its repressors PER and TIM are under tight transcriptional control. However, posttranslational modification of these proteins and regulation of their stability are critical to their function and to the generation of 24-hr period rhythms. We review here recent progress made in our understanding of PER, TIM and CLK posttranslational control. We also review recent studies that are uncovering the importance of novel regulatory mechanisms that affect mRNA stability and translation of circadian pacemaker proteins and their output.
Figures
References
-
- Crane BR, Young MW. Interactive features of proteins composing eukaryotic circadian clocks. Annu Rev Biochem. 2014;83:191–219. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Emery P. Molecular and neural control of insects circadian rhythms. In: Gilbert LI, editor. Insect Molecular Biology and Biochemistry. New York: Academic Press; 2012. pp. 513–551. Edited by: vol.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

