Expression of Notch1 Correlates with Breast Cancer Progression and Prognosis
- PMID: 26121683
- PMCID: PMC4488260
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131689
Expression of Notch1 Correlates with Breast Cancer Progression and Prognosis
Abstract
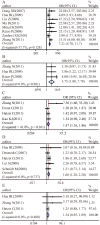
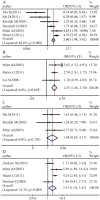
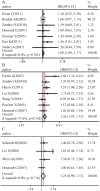
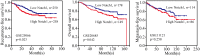
Various studies have evaluated the significance of Notch1 expression in breast cancer, but the results have ever been disputed. By using 21 studies involving 3867 patients, this meta-analysis revealed that the expression of Notch1 was significantly higher in breast cancer than in normal tissues (OR=7.21; 95%CI, 4.7-11.07) and that higher Notch1 expression was associated with transition from ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) to invasive cancer (OR=3.75; 95% CI, 1.8-7.78). Higher Notch1 activity was observed in the basal subtype of breast cancer (OR=2.53; 95% CI, 1.18-5.43). Moreover, patients with Notch1 overexpression exhibited significantly worse overall and recurrence-free survival. Our meta-analysis suggests that Notch inhibitors may be useful in blocking the early progression of DCIS and that the outcomes of clinical trials for Notch1-targeting therapeutics could be improved by the molecular stratification of breast cancer patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Grabher C, von Boehmer H, Look AT. Notch 1 activation in the molecular pathogenesis of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006; 6: 347–359. - PubMed
-
- Gallahan D, Callahan R. The mouse mammary tumor associated gene INT3 is a unique member of the NOTCH gene family (NOTCH4). Oncogene. 1997; 14: 1883–1890. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

