Persistent Pneumonia in an Infant
- PMID: 26122810
- PMCID: PMC4485008
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2014-3856
Persistent Pneumonia in an Infant
Abstract
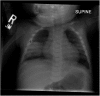
A 4-month-old boy with past medical history of eczema presented with fever and cough; a chest radiograph showed lung consolidation, and he was initially treated with amoxicillin for presumed community-acquired pneumonia. After several days, his fever persisted. He was also profoundly anemic. Antibiotic coverage was broadened because of the concern for resistant organisms; he began to improve and was discharged from the hospital. However, at 5 months of age, his fever returned, and he continued to demonstrate lung consolidation on chest radiograph. Additionally, he had lost weight and continued to be anemic. Splenic cysts were noted on abdominal ultrasound. He was diagnosed with an unusual etiology for his pneumonia and improved with the appropriate therapy. An underlying immunodeficiency was suspected, but initial testing was nondiagnostic. At 12 months of age, he presented with another infection, and the final diagnosis was made.
Copyright © 2015 by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Figures


References
-
- Bradley JS, Byington CL, Shah SS, et al. ; Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society and the Infectious Diseases Society of America. The management of community-acquired pneumonia in infants and children older than 3 months of age: clinical practice guidelines by the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society and the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;53(7):e25–e76 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jeffery Modell Foundation. Ten warning signs for primary immunodeficiency. Available at: http://downloads.info4pi.org/pdfs/General10WarningSignsFINAL.pdf
-
- Immunology deficiency search database. Available at: http://www.immunodeficiencysearch.com/home. 2015
-
- Thorell E. Cervical lymphadenitis and neck infections. In Long S, Pickering L, Prober C, eds. Principles and Practice of Pediatric Infectious Disease. 4th ed. New York, NY: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone; 2012;135–147
-
- Gigliotti F, Wright TW. Pneumocystis jirovecci. In Kliegman R, Nelson WE, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 19th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders; 2011:1069e1–1069e5
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

