The ribosomal S10 protein is a general target for decreased tigecycline susceptibility
- PMID: 26124155
- PMCID: PMC4538488
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00547-15
The ribosomal S10 protein is a general target for decreased tigecycline susceptibility
Abstract
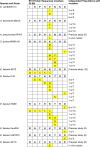
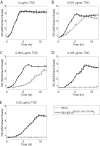
Tigecycline is a translational inhibitor with efficacy against a wide range of pathogens. Using experimental evolution, we adapted Acinetobacter baumannii, Enterococcus faecium, Escherichia coli, and Staphylococcus aureus to growth in elevated tigecycline concentrations. At the end of adaptation, 35 out of 47 replicate populations had clones with a mutation in rpsJ, the gene that encodes the ribosomal S10 protein. To validate the role of mutations in rpsJ in conferring tigecycline resistance, we showed that mutation of rpsJ alone in Enterococcus faecalis was sufficient to increase the tigecycline MIC to the clinical breakpoint of 0.5 μg/ml. Importantly, we also report the first identification of rpsJ mutations associated with decreased tigecycline susceptibility in A. baumannii, E. coli, and S. aureus. The identified S10 mutations across both Gram-positive and -negative species cluster in the vertex of an extended loop that is located near the tigecycline-binding pocket within the 16S rRNA. These data indicate that S10 is a general target of tigecycline adaptation and a relevant marker for detecting reduced susceptibility in both Gram-positive and -negative pathogens.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

References
-
- CDC. 2013. Antibiotic resistance threat report. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, GA: http://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/threat-report-2013/.
-
- McAleese F, Petersen P, Ruzin A, Dunman PM, Murphy E, Projan SJ, Bradford PA. 2005. A novel MATE family efflux pump contributes to the reduced susceptibility of laboratory-derived Staphylococcus aureus mutants to tigecycline. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:1865–1871. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.5.1865-1871.2005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

