Therapeutic effects of C-28 methyl ester of 2-cyano-3,12-dioxoolean-1,9-dien-28-oic acid (CDDO-Me; bardoxolone methyl) on radiation-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis in mice
- PMID: 26124639
- PMCID: PMC4482372
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S80958
Therapeutic effects of C-28 methyl ester of 2-cyano-3,12-dioxoolean-1,9-dien-28-oic acid (CDDO-Me; bardoxolone methyl) on radiation-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis in mice
Abstract
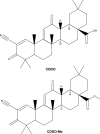
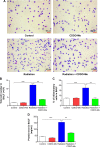
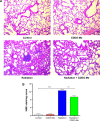
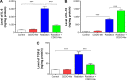
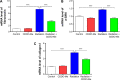
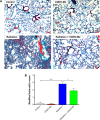
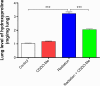
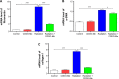
The C-28 methyl ester of 2-cyano-3,12-dioxoolean-1,9-dien-28-oic acid (CDDO-Me), one of the synthetic triterpenoids, has been found to have potent anti-inflammatory and anticancer properties in vitro and in vivo. However, its usefulness in mitigating radiation-induced lung injury (RILI), including radiation-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis, has not been tested. The aim of this study was to explore the therapeutic effect of CDDO-Me on RILI in mice and the underlying mechanisms. Herein, we found that administration of CDDO-Me improved the histopathological score, reduced the number of inflammatory cells and concentrations of total protein in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, suppressed secretion and expression of proinflammatory cytokines, including transforming growth factor-β and interleukin-6, elevated expression of the anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-10, and downregulated the mRNA level of profibrotic genes, including for fibronectin, α-smooth muscle actin, and collagen I. CDDO-Me attenuated radiation-induced lung inflammation. CDDO-Me also decreased the Masson's trichrome stain score, hydroxyproline content, and mRNA level of profibrotic genes, and blocked radiation-induced collagen accumulation and fibrosis. Collectively, these findings suggest that CDDO-Me ameliorates radiation-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis, and this synthetic triterpenoid is a promising novel therapeutic agent for RILI. Further mechanistic, efficacy, and safety studies are warranted to elucidate the role of CDDO-Me in the management of RILI.
Keywords: CDDO-Me; cytokine; fibrosis; inflammation; mouse; radiation-induced lung injury; radiotherapy; transforming growth factor-β.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The triterpenoid CDDO-Me inhibits bleomycin-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis.PLoS One. 2013 May 31;8(5):e63798. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063798. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23741300 Free PMC article.
-
The synthetic triterpenoid CDDO-methyl ester modulates microglial activities, inhibits TNF production, and provides dopaminergic neuroprotection.J Neuroinflammation. 2008 May 12;5:14. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-5-14. J Neuroinflammation. 2008. PMID: 18474101 Free PMC article.
-
Bardoxolone methyl induces apoptosis and autophagy and inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stemness in esophageal squamous cancer cells.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Feb 17;9:993-1026. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S73493. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 25733817 Free PMC article.
-
Bardoxolone methyl (CDDO-Me) as a therapeutic agent: an update on its pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014 Oct 23;8:2075-88. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S68872. eCollection 2014. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014. PMID: 25364233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis and Anticancer Activity of CDDO and CDDO-Me, Two Derivatives of Natural Triterpenoids.Molecules. 2019 Nov 13;24(22):4097. doi: 10.3390/molecules24224097. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31766211 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chinese Herbs and Repurposing Old Drugs as Therapeutic Agents in the Regulation of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Pulmonary Diseases.J Inflamm Res. 2021 Mar 4;14:657-687. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S293135. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 33707963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of natural products in revealing NRF2 function.Nat Prod Rep. 2020 Jun 1;37(6):797-826. doi: 10.1039/c9np00061e. Epub 2020 May 13. Nat Prod Rep. 2020. PMID: 32400766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Nexus of Inflammation-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Lung Cancer Progression: A Roadmap to Pentacyclic Triterpenoid-Based Therapies.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 10;24(24):17325. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417325. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of RTA 404 in Human Brain Malignant Glioma Cell Lines via Cell Cycle Arrest via p21/AKT Signaling.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Mar 8;2021:5552226. doi: 10.1155/2021/5552226. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33763472 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Nrf2/PIWIL2/purine metabolism axis in controlling radiation-induced lung fibrosis.Am J Cancer Res. 2020 Sep 1;10(9):2752-2767. eCollection 2020. Am J Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33042615 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kong FM, Zhao L, Hayman JA. The role of radiation therapy in thoracic tumors. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2006;20(2):363–400. - PubMed
-
- Rodrigues G, Movsas B. Future directions in palliative thoracic radiotherapy. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2012;6(1):91–96. - PubMed
-
- Videtic GM. The role of radiation therapy in small cell lung cancer. Curr Oncol Rep. 2013;15(4):405–410. - PubMed
-
- Delaney G, Jacob S, Featherstone C, Barton M. The role of radiotherapy in cancer treatment: estimating optimal utilization from a review of evidence-based clinical guidelines. Cancer. 2005;104(6):1129–1137. - PubMed
-
- Marks LB, Yu X, Vujaskovic Z, Small W, Jr, Folz R, Anscher MS. Radiation-induced lung injury. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2003;13(3):333–345. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

