Perspectives on the revised Ghent criteria for the diagnosis of Marfan syndrome
- PMID: 26124674
- PMCID: PMC4476478
- DOI: 10.2147/TACG.S60472
Perspectives on the revised Ghent criteria for the diagnosis of Marfan syndrome
Abstract
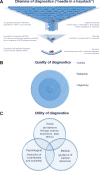
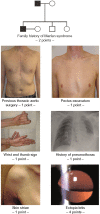
Three international nosologies have been proposed for the diagnosis of Marfan syndrome (MFS): the Berlin nosology in 1988; the Ghent nosology in 1996 (Ghent-1); and the revised Ghent nosology in 2010 (Ghent-2). We reviewed the literature and discussed the challenges and concepts of diagnosing MFS in adults. Ghent-1 proposed more stringent clinical criteria, which led to the confirmation of MFS in only 32%-53% of patients formerly diagnosed with MFS according to the Berlin nosology. Conversely, both the Ghent-1 and Ghent-2 nosologies diagnosed MFS, and both yielded similar frequencies of MFS in persons with a causative FBN1 mutation (90% for Ghent-1 versus 92% for Ghent-2) and in persons not having a causative FBN1 mutation (15% versus 13%). Quality criteria for diagnostic methods include objectivity, reliability, and validity. However, the nosology-based diagnosis of MFS lacks a diagnostic reference standard and, hence, quality criteria such as sensitivity, specificity, or accuracy cannot be assessed. Medical utility of diagnosis implies congruency with the historical criteria of MFS, as well as with information about the etiology, pathogenesis, diagnostic triggers, prognostic triggers, and potential complications of MFS. In addition, social and psychological utilities of diagnostic criteria include acceptance by patients, patient organizations, clinicians and scientists, practicability, costs, and the reduction of anxiety. Since the utility of a diagnosis or exclusion of MFS is context-dependent, prioritization of utilities is a strategic decision in the process of nosology development. Screening tests for MFS should be used to identify persons with MFS. To confirm the diagnosis of MFS, Ghent-1 and Ghent-2 perform similarly, but Ghent-2 is easier to use. To maximize the utility of the diagnostic criteria of MFS, a fair and transparent process of nosology development is essential.
Keywords: FBN1; Ghent nosology; Marfan syndrome; aorta; diagnosis; mutation.
Figures
References
-
- Murdoch JL, Walker BA, Halpern BL, Kuzma JW, McKusick VA. Life expectancy and causes of death in the Marfan syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1972;286(15):804–808. - PubMed
-
- Rand-Hendriksen S, Sørensen I, Holmström H, Andersson S, Finset A. Fatigue, cognitive functioning and psychological distress in Marfan syndrome, a pilot study. Psychol Health Med. 2007;12(3):305–313. - PubMed
-
- Bathen T, Velvin G, Rand-Hendriksen S, Robinson HS. Fatigue in adults with Marfan syndrome, occurrence and associations to pain and other factors. Am J Med Genet A. 2014;164A(8):1931–1939. - PubMed
-
- Peters KF, Kong F, Horne R, Francomano CA, Biesecker BB. Living with Marfan syndrome I. Perceptions of the condition. Clin Genet. 2001;60(4):273–282. - PubMed
-
- Peters KF, Petrill SA. Comparison of the background, needs, and expectations for genetic counseling of adults with experience with Down syndrome, Marfan syndrome, and neurofibromatosis. Am J Med Genet A. 2011;155A(4):684–696. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

