Factors Predicting Therapeutic Efficacy of Combination Treatment With Sitagliptin and Insulin in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: The ASSIST-K Study
- PMID: 26124906
- PMCID: PMC4471747
- DOI: 10.14740/jocmr2149w
Factors Predicting Therapeutic Efficacy of Combination Treatment With Sitagliptin and Insulin in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: The ASSIST-K Study
Abstract
Background: It is unclear whether dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors decrease hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) in a glucose-dependent manner in patients on insulin therapy who have impaired insulin secretion. This study investigated factors influencing the efficacy of sitagliptin when used concomitantly with insulin to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in the real-world setting.
Methods: A retrospective study was conducted of 1,004 T2DM patients at 36 Japanese clinics associated with the Diabetes Task Force of the Kanagawa Physicians Association. Eligible patients had been on insulin for at least 6 months, with a baseline HbA1c of 7.0% (53 mmol/mol) or higher. Baseline characteristics and laboratory data from 495 patients were subjected to multiple regression analysis to identify factors influencing the change of HbA1c.
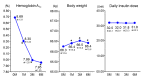
Results: Most patients (n = 809) received sitagliptin at a dose of 50 mg. In the 1,004 patients, HbA1c decreased by 0.74% (6 mmol/mol) and body weight increased by 0.1 kg after 6 months of combination therapy. Multiple regression analysis showed that a higher baseline HbA1c, older age, and lower body mass index influenced the change of HbA1c after 6 months. Hypoglycemic symptoms occurred in 7.4%, but none were severe.
Conclusions: These results emphasize the importance of a higher HbA1c at the commencement of sitagliptin therapy in patients on insulin. Glucose-dependent suppression of glucagon secretion by sitagliptin may be useful in patients with impaired insulin secretion. Sitagliptin can be used concomitantly with insulin irrespective of the insulin regimen, duration of insulin treatment, and concomitant medications.
Keywords: Body weight; Combination therapy; HbA1c; Insulin; Multiple regression analysis; Sitagliptin; Type 2 diabetes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Factor Analysis of Changes in Hemoglobin A1c After 12 Months of Sitagliptin Therapy in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes.J Clin Med Res. 2016 Jun;8(6):461-71. doi: 10.14740/jocmr2540w. Epub 2016 May 25. J Clin Med Res. 2016. PMID: 27222674 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Adding Sitagliptin in Type 2 Diabetes Patients on Insulin: Age-Stratified Comparison at One Year in the ASSIST-K Study.J Clin Med Res. 2019 May;11(5):311-320. doi: 10.14740/jocmr3677. Epub 2019 Apr 14. J Clin Med Res. 2019. PMID: 31019624 Free PMC article.
-
Medium-Term Effect of Add-On Therapy with the DPP-4 Inhibitor, Sitagliptin, in Insulin-Treated Japanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Diabetes Ther. 2016 Jun;7(2):309-20. doi: 10.1007/s13300-016-0170-2. Epub 2016 Apr 25. Diabetes Ther. 2016. PMID: 27114254 Free PMC article.
-
Sitagliptin: Profile of a novel DPP-4 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.Drugs Today (Barc). 2007 Jan;43(1):13-25. doi: 10.1358/dot.2007.43.1.1043909. Drugs Today (Barc). 2007. PMID: 17315049 Review.
-
Sitagliptin: profile of a novel DPP-4 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes (update).Drugs Today (Barc). 2007 Nov;43(11):801-14. doi: 10.1358/dot.2007.43.11.1157620. Drugs Today (Barc). 2007. PMID: 18174966 Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness and Safety of Sitagliptin in Patients with Beta-thalassaemia Major and Diabetes Mellitus: A Case Series.Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2017 Jan 1;9(1):e2017004. doi: 10.4084/MJHID.2017.004. eCollection 2017. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28101310 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of the effect on antihyperglycaemic action of sitagliptin by plasma active form glucagon-like peptide-1.World J Diabetes. 2016 Jun 10;7(11):230-8. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i11.230. Epub 2016 Jun 11. World J Diabetes. 2016. PMID: 27326345 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Once-Weekly Dulaglutide in Type 2 Diabetes Patients Using Insulin: Exploratory Subgroup Analysis by Insulin Regimen.Diabetes Ther. 2020 Mar;11(3):735-745. doi: 10.1007/s13300-020-00765-6. Epub 2020 Jan 29. Diabetes Ther. 2020. PMID: 31994009 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Voluntary Participation on Mobile Health Care in Diabetes Management: Randomized Controlled Open-Label Trial.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020 Sep 18;8(9):e19153. doi: 10.2196/19153. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020. PMID: 32945775 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Study of Seasonal Variation in the Effect of Add-On Sitagliptin on Blood Glucose Control in Insulin-Treated Patients With Type 2 Diabetes.J Clin Med Res. 2020 Mar;12(3):200-208. doi: 10.14740/jocmr4103. Epub 2020 Mar 2. J Clin Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32231757 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Umpierrez GE, Gianchandani R, Smiley D, Jacobs S, Wesorick DH, Newton C, Farrokhi F. et al. Safety and efficacy of sitagliptin therapy for the inpatient management of general medicine and surgery patients with type 2 diabetes: a pilot, randomized, controlled study. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(11):3430–3435. doi: 10.2337/dc13-0277. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shimoda S, Iwashita S, Ichimori S, Matsuo Y, Goto R, Maeda T, Matsuo T. et al. Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin as add-on therapy on glycemic control and blood glucose fluctuation in Japanese type 2 diabetes subjects ongoing with multiple daily insulin injections therapy. Endocr J. 2013;60(10):1207–1214. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ13-0198. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mori Y, Taniguchi Y, Miyazaki S, Yokoyama J, Utsunomiya K. Effects of add-on treatment with sitagliptin on narrowing the range of glucose fluctuations in Japanese type 2 diabetes patients receiving insulin therapy. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2013;15(3):237–240. doi: 10.1089/dia.2012.0214. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kadowaki T, Tajima N, Odawara M, Minamide T, Kawashima M, Yanagida D, Okamoto T. et al. Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin add-on therapy in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes on insulin monotherapy. Diabetol Int. 2013;4:160–172. doi: 10.1007/s13340-013-0109-z. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources