miR-122 Regulates LH Receptor Expression by Activating Sterol Response Element Binding Protein in Rat Ovaries
- PMID: 26125464
- PMCID: PMC4541618
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2015-1121
miR-122 Regulates LH Receptor Expression by Activating Sterol Response Element Binding Protein in Rat Ovaries
Abstract
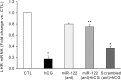
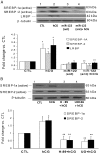
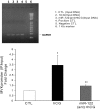
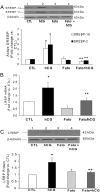
LH/human chorionic gonadotropin receptor (LHR) undergoes down-regulation during preovulatory LH surge or in response to exposure to a supraphysiological concentration of its ligands through a posttranscriptional mechanism involving an RNA binding protein designated as LHR mRNA binding protein (LRBP). miR-122, a short noncoding RNA, has been shown to mediate the up-regulation of LRBP. In the present study, we show that inhibition of miR-122 using a locked nucleic acid (LNA)-conjugated antagomir suppressed human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)-induced up-regulation of LRBP as well as its association with LHR mRNA, as analyzed by RNA EMSA. Most importantly, inhibition of miR-122 resulted in the abolishment of hCG-mediated LHR mRNA down-regulation. We also show that the transcription factor, sterol regulatory element binding protein (SREBP) (SREBP-1a and SREBP-2 isoforms), is an intermediate in miR-122-mediated LHR mRNA regulation. HCG-stimulated increase in the activation of both SREBP-1a and SREBP-2 was inhibited by pretreatment with the miR-122 antagomir. The inhibition of cAMP/protein kinase A (PKA) and ERK pathways, upstream activators of miR-122, abolished SREBP activation after hCG treatment. SREBP-mediated regulation of LRBP expression is mediated by recruitment of LRBP promoter element to SREBP-1a, because chromatin immunoprecipitation assay revealed that association of LRBP promoter to SREBP was increased by hCG treatment. Pretreatment with miR-122 antagomir suppressed this response. Inhibition of SREBP activation by pretreating the rats with a chemical compound, fatostatin abrogated hCG-induced up-regulation of LRBP mRNA and protein. Fatostatin also inhibited LHR-LRBP mRNA-protein complex formation and LHR down-regulation. These results conclusively show that miR-122 plays a regulatory role in LH/hCG-induced LHR mRNA down-regulation by increasing LRBP expression through the activation of SREBP pathway.
Figures




References
-
- McFarland KC, Sprengel R, Phillips HS, et al. Lutropin-choriogonadotropin receptor: an unusual member of the G protein-coupled receptor family. Science. 1989;245(4917):494–499. - PubMed
-
- Loosfelt H, Misrahi M, Atger M, et al. Cloning and sequencing of porcine LH-hCG receptor cDNA: variants lacking transmembrane domain. Science. 1989;245(4917):525–528. - PubMed
-
- LaPolt PS, Oikawa M, Jia XC, Dargan C, Hsueh AJ. Gonadotropin-induced up- and down-regulation of rat ovarian LH receptor message levels during follicular growth, ovulation and luteinization. Endocrinology. 1990;126(6):3277–3279. - PubMed
-
- Segaloff DL, Wang HY, Richards JS. Hormonal regulation of luteinizing hormone/chorionic gonadotropin receptor mRNA in rat ovarian cells during follicular development and luteinization. Mol Endocrinol. 1990;4(12):1856–1865. - PubMed
-
- Hoffman YM, Peegel H, Sprock MJ, Zhang QY, Menon KMJ. Evidence that human chorionic gonadotropin/luteinizing hormone receptor down-regulation involves decreased levels of receptor messenger ribonucleic acid. Endocrinology. 1991;128(1):388–393. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

