Ameloblastic Carcinoma
- PMID: 26126621
- PMCID: PMC4492487
- DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.893918
Ameloblastic Carcinoma
Abstract
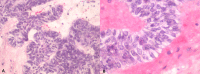
Background: Ameloblastic carcinoma secondary type is an extremely rare and aggressive odontogenic neoplasm that exhibits histological features of malignancy in primary and metastatic sites. It arises through carcinomatous de-differentiation of a pre-existing ameloblastoma or odontogenic cyst, typically following repeated treatments and recurrences of the benign precursor neoplasm. Identification of an ameloblastic carcinoma, secondary type presenting with histologic features of malignant transformation from an earlier untreated benign lesion remains a rarity. Herein, we report 1 such case.
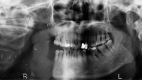
Case report: A 66-year-old man was referred for management of a newly diagnosed ameloblastic carcinoma. He underwent radical surgical intervention comprising hemimandibulectomy, supraomohyoid neck dissection, and free-flap reconstruction. Final histologic analysis demonstrated features suggestive of carcinomatous de-differentiation for a consensus diagnosis of ameloblastic carcinoma, secondary type (de-differentiated) intraosseous.
Conclusions: Ameloblastic carcinoma, secondary type represents a rare and challenging histologic diagnosis. Radical surgical resection with adequate hard and soft tissue margins is essential for curative management of localized disease.
Figures


References
-
- Sciubba JJ, Eversole LR, Slootweg PJ. Odontogenic/ameloblastic carcinomas. In: Barnes L, Eveson JW, Reichart P, et al., editors. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours Pathology and Genetics of Head and Neck Tumours. Lyon: IARC Press; 2005. pp. 287–89.
-
- Shafer W, Hine M, Levy B. A textbook of Oral Pathology. 4th ed. USA: WB Saunders; 1974.
-
- Slootweg PJ, Muller H. Malignant ameloblastoma or ameloblastic carcinoma. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1984;57:168–76. - PubMed
-
- Elzay RP. Primary intraosseous carcinoma of the jaws. Review and update of odontogenic carcinomas. Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1982;54:299–303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

