Generation and transcriptional programming of intestinal dendritic cells: essential role of retinoic acid
- PMID: 26129652
- PMCID: PMC4698111
- DOI: 10.1038/mi.2015.50
Generation and transcriptional programming of intestinal dendritic cells: essential role of retinoic acid
Abstract
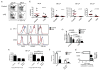
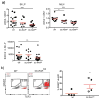
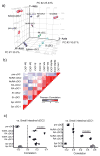
The vitamin A metabolite retinoic acid (RA) regulates adaptive immunity in the intestines, with well-characterized effects on IgA responses, Treg induction, and gut trafficking of T- and B-effector cells. It also controls the generation of conventional dendritic cell (cDC) precursors in the bone marrow and regulates cDC subset representation, but its roles in the specialization of intestinal cDC subsets are understudied. Here we show that RA acts cell intrinsically in developing gut-tropic pre-mucosal dendritic cell (pre-μDC) to effect the differentiation and drive the specialization of intestinal CD103(+)CD11b(-) (cDC1) and of CD103(+)CD11b(+) (cDC2). Systemic deficiency or DC-restricted antagonism of RA signaling resulted in altered phenotypes of intestinal cDC1 and cDC2, and reduced numbers of cDC2. Effects of dietary deficiency were most apparent in the proximal small intestine and were rapidly reversed by reintroducing vitamin A. In cultures of pre-μDC with Flt3L and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), RA induced cDC with characteristic phenotypes of intestinal cDC1 and cDC2 by controlling subset-defining cell surface receptors, regulating subset-specific transcriptional programs, and suppressing proinflammatory nuclear factor-κB-dependent gene expression. Thus, RA is required for transcriptional programming and maturation of intestinal cDC, and with GM-CSF and Flt3L provides a minimal environment for in vitro generation of intestinal cDC1- and cDC2-like cDC from specialized precursors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no conflicts.
Figures


References
-
- Crozat K, Tamoutounour S, Vu Manh TP, et al. Cutting edge: expression of XCR1 defines mouse lymphoid-tissue resident and migratory dendritic cells of the CD8alpha+ type. J Immunol. 2011 Nov 1;187(9):4411–4415. - PubMed
-
- Zhang JG, Czabotar PE, Policheni AN, et al. The dendritic cell receptor Clec9A binds damaged cells via exposed actin filaments. Immunity. 2012 Apr 20;36(4):646–657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

