BioMaS: a modular pipeline for Bioinformatic analysis of Metagenomic AmpliconS
- PMID: 26130132
- PMCID: PMC4486701
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-015-0595-z
BioMaS: a modular pipeline for Bioinformatic analysis of Metagenomic AmpliconS
Abstract
Background: Substantial advances in microbiology, molecular evolution and biodiversity have been carried out in recent years thanks to Metagenomics, which allows to unveil the composition and functions of mixed microbial communities in any environmental niche. If the investigation is aimed only at the microbiome taxonomic structure, a target-based metagenomic approach, here also referred as Meta-barcoding, is generally applied. This approach commonly involves the selective amplification of a species-specific genetic marker (DNA meta-barcode) in the whole taxonomic range of interest and the exploration of its taxon-related variants through High-Throughput Sequencing (HTS) technologies. The accessibility to proper computational systems for the large-scale bioinformatic analysis of HTS data represents, currently, one of the major challenges in advanced Meta-barcoding projects.
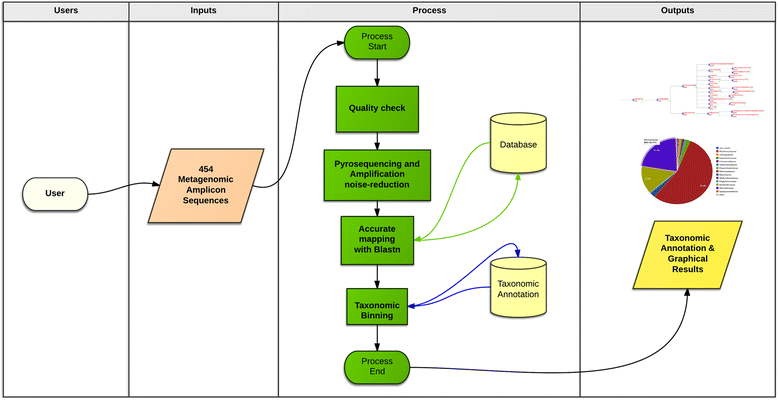
Results: BioMaS (Bioinformatic analysis of Metagenomic AmpliconS) is a new bioinformatic pipeline designed to support biomolecular researchers involved in taxonomic studies of environmental microbial communities by a completely automated workflow, comprehensive of all the fundamental steps, from raw sequence data upload and cleaning to final taxonomic identification, that are absolutely required in an appropriately designed Meta-barcoding HTS-based experiment. In its current version, BioMaS allows the analysis of both bacterial and fungal environments starting directly from the raw sequencing data from either Roche 454 or Illumina HTS platforms, following two alternative paths, respectively. BioMaS is implemented into a public web service available at https://recasgateway.ba.infn.it/ and is also available in Galaxy at http://galaxy.cloud.ba.infn.it:8080 (only for Illumina data).
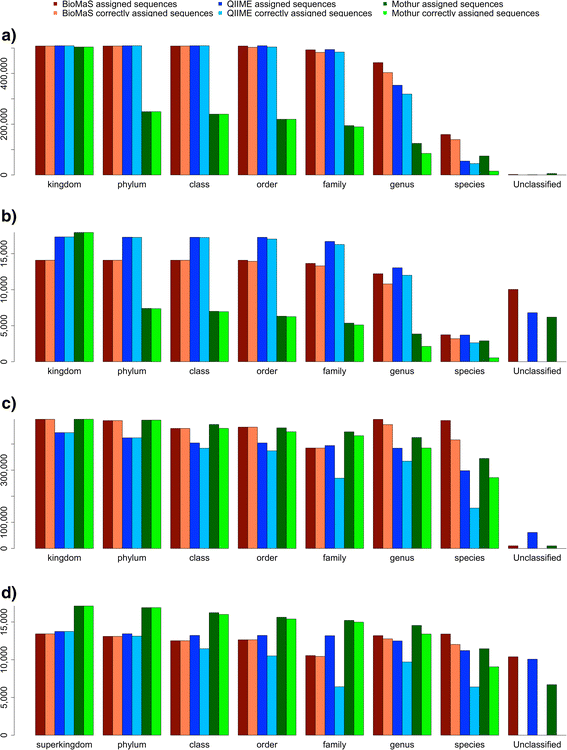
Conclusion: BioMaS is a friendly pipeline for Meta-barcoding HTS data analysis specifically designed for users without particular computing skills. A comparative benchmark, carried out by using a simulated dataset suitably designed to broadly represent the currently known bacterial and fungal world, showed that BioMaS outperforms QIIME and MOTHUR in terms of extent and accuracy of deep taxonomic sequence assignments.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MG-RAST, a Metagenomics Service for Analysis of Microbial Community Structure and Function.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1399:207-33. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3369-3_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26791506
-
e-DNA meta-barcoding: from NGS raw data to taxonomic profiling.Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1269:257-78. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2291-8_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25577384
-
BIOCOM-PIPE: a new user-friendly metabarcoding pipeline for the characterization of microbial diversity from 16S, 18S and 23S rRNA gene amplicons.BMC Bioinformatics. 2020 Oct 31;21(1):492. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-03829-3. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 33129268 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental microbiology through the lens of high-throughput DNA sequencing: synopsis of current platforms and bioinformatics approaches.J Microbiol Methods. 2012 Oct;91(1):106-13. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2012.07.017. Epub 2012 Jul 28. J Microbiol Methods. 2012. PMID: 22849829 Review.
-
Practical considerations for sampling and data analysis in contemporary metagenomics-based environmental studies.J Microbiol Methods. 2018 Nov;154:14-18. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2018.09.020. Epub 2018 Oct 1. J Microbiol Methods. 2018. PMID: 30287354 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA Metabarcoding for the Characterization of Terrestrial Microbiota-Pitfalls and Solutions.Microorganisms. 2021 Feb 12;9(2):361. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9020361. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33673098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accurate quantification of bacterial abundance in metagenomic DNAs accounting for variable DNA integrity levels.Microb Genom. 2020 Oct;6(10):mgen000417. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000417. Microb Genom. 2020. PMID: 32749951 Free PMC article.
-
Unbiased Taxonomic Annotation of Metagenomic Samples.J Comput Biol. 2018 Mar;25(3):348-360. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2017.0144. Epub 2017 Oct 13. J Comput Biol. 2018. PMID: 29028181 Free PMC article.
-
Fungal metabarcoding data integration framework for the MycoDiversity DataBase (MDDB).J Integr Bioinform. 2020 May 28;17(1):20190046. doi: 10.1515/jib-2019-0046. J Integr Bioinform. 2020. PMID: 32463383 Free PMC article.
-
Complexity and Dynamics of the Winemaking Bacterial Communities in Berries, Musts, and Wines from Apulian Grape Cultivars through Time and Space.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 14;11(6):e0157383. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157383. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27299312 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pearson WR, Robins G, Wrege DE, Zhang TT. On the primer selection problem in polymerase chain reaction experiments. Discrete Appl Math. 1996;71(1–3):231–46. doi: 10.1016/S0166-218X(96)00066-2. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

