Investigation of RNA interference suppression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in mouse model of atherosclerosis
- PMID: 26131101
- PMCID: PMC4484024
Investigation of RNA interference suppression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in mouse model of atherosclerosis
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effect of RNA interference of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 on atherosclerosis on atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E (ApoE)-/- mouse.
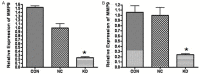
Methods: ApoE-/- mouse strain and three cell lines (293T, NIH3T3 and Raw264.7) were used in the present study to investigate the effect of MMP-9 silencing by RNA interference. Thirty 10-week-old ApoE-/- mice were randomly assigned to a control group, lentiviruses with naked vector group and Lentiviruses-MMP-9 intervention group (n = 10). Aortic atherosclerotic plaques of the mice were stained with immunohistochemical techniques, the MMP-9 and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels of three groups were detected simultaneously. Expression of MMP-9 was significantly down-regulated in interference group. MMP-9 and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels in MMP-9 interference group were significantly lower than that of the control group.
Conclusion: The expression of MMP-9 is closely related to vulnerability of atherosclerotic plaques. Silencing of MMP-9 expression acts as a positive role in maintenance of atherosclerotic plaque stability. The present study provides novel experimental insight for the treatment of vulnerable plaques in atherosclerosis.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; MMP-9; RNA interference; vulnerability.
Figures
References
-
- Ambrose JA, Tannenbaum MA, Alexopoulos D, Hjemdahl-Monsen CE, Leavy J, Weiss M, Borrico S, Gorlin R, Fuster V. Angiographic progression of coronary artery disease and the development of myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1988;12:56–62. - PubMed
-
- Virmani R, Burke AP, Farb A, Kolodgie FD. Pathology of the vulnerable plaque. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47:C13–18. - PubMed
-
- Dabek J, Kulach A, Gasior Z. The role of matrix metalloproteinases in acute coronary syndromes. Eur J Intern Med. 2007;18:463–466. - PubMed
-
- Visse R, Nagase H. Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: structure, function, and biochemistry. Circ Res. 2003;92:827–839. - PubMed
-
- Galis ZS, Johnson C, Godin D, Magid R, Shipley JM, Senior RM, Ivan E. Targeted disruption of the matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene impairs smooth muscle cell migration and geometrical arterial remodeling. Circ Res. 2002;91:852–859. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
