Recent progress in the diagnosis and treatment of posterior tibial plateau fractures
- PMID: 26131147
- PMCID: PMC4484037
Recent progress in the diagnosis and treatment of posterior tibial plateau fractures
Abstract
The posterior tibial plateau fracture is drawing increasing attention from orthopedists in recent years with the popularity of CT. However, due to the particular and severity of posterior tibial plateau fracture, there is still controversy in its classification and treatment. It is very difficult to achieve the ideal reduction and fixation by conventional techniques and approaches. The modified posterior approach is favorable for posterior tibial plateau fracture, but disadvantages remain. Recently, the lateral approach is applied by doctors. It is ideal for treatment of posterior tibial plateau fracture. Because of the complexity of local anatomical structure, the operative management of posterior tibial plateau fractures is a contentious issue as revealed in the recent surge of published literature addressing the surgical approach. This review mainly summaries the diagnosis, classification and surgery of the posterior tibial plateau fractures.
Keywords: Tibial plateau; diagnosis; fracture; operative approach.
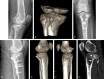
Figures


References
-
- Borrelli J Jr. Management of soft tissue injuries associated with tibial plateau fractures. J Knee Surg. 2014;27:5–9. - PubMed
-
- Choo KJ, Morshed S. Postoperative complications after repair of tibial plateau fractures. J Knee Surg. 2014;27:11–19. - PubMed
-
- Burdin G. Arthroscopic management of tibial plateau fractures: surgical technique. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013;99:S208–S218. - PubMed
-
- Zhang CC. Diagnosis and therapy of tibial plateau fractures and Pilon fractures. Chin J Orhto Traumatol. 2010;23:81–83. - PubMed
-
- Markhardt BK, Gross JM, Monu J. Schatzker classification of tibial plateau fractures: use of CT and MR imaging improves assessment. Radiographics. 2009;29:585–597. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
