Accessory Gene Regulator Polymorphism and Vancomycin Minimum Inhibitory Concentration in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 26131410
- PMCID: PMC4446577
- DOI: 10.3343/alm.2015.35.4.399
Accessory Gene Regulator Polymorphism and Vancomycin Minimum Inhibitory Concentration in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
Background: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacteremia with a vancomycin minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 2 µg/mL presents a high rate of therapeutic failure in response to vancomycin. In addition, polymorphism in accessory gene regulator (agr) is associated with vancomycin therapeutic effects. The association between agr polymorphism and vancomycin MICs was investigated in MRSA isolates.
Methods: Agr group-specific PCR was conducted on 118 MRSA bloodstream isolates. Vancomycin susceptibility tests were conducted, while E-test GRD (bioMérieux SA, France) was used to detect heterogeneous vancomycin-intermediate S. aureus (hVISA).
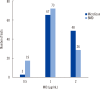
Results: Of the 118 MRSA isolates, 59 (50.0%), 43 (36.4%), and 10 (8.5%) isolates belonged to agr group I, II, and III, respectively. Six isolates could not be classified. Twenty-six, 73, and 19 isolates presented a vancomycin MIC of 2, 1, and 0.5 µg/mL, respectively. Nine (34.6%), 14 (53.8%), and 2 (7.7%) isolates with MICs of 2 µg/mL belonged to agr group I, II, and III, respectively. Thirty-seven (50.6%), 26 (35.6%), and 6 (8.2%) isolates with MICs of 1 µg/mL belonged to agr group I, II, and III, respectively. Thirteen (68.4%), 3 (15.8%), and 2 (10.5%) isolates with MICs of 0.5 µg/mL belonged to agr group I, II, and III, respectively. The agr group II presented more isolates with MIC of 2 µg/mL (32.6%) than the agr non-group II (16%). Four isolates tested positive for hVISA. Three of them belonged to agr group II.
Conclusions: MRSA isolates with vancomycin MIC of 2 µg/mL were more common in agr group II than in agr non-group II.
Keywords: Agr polymorphism; Staphylococcus aureus; Vancomycin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vancomycin MIC and agr dysfunction in invasive MRSA infections in southern Brazil.Braz J Microbiol. 2020 Dec;51(4):1819-1823. doi: 10.1007/s42770-020-00384-0. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Braz J Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33074551 Free PMC article.
-
Is there a clinical association of vancomycin MIC creep, agr group II locus, and treatment failure in MRSA bacteremia?Diagn Mol Pathol. 2011 Sep;20(3):184-8. doi: 10.1097/PDM.0b013e318208fc47. Diagn Mol Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21817905
-
Trend in vancomycin susceptibility and correlation with molecular characteristics of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus causing invasive infections in Taiwan: results from the Tigecycline in vitro Surveillance in Taiwan (TIST) study, 2006-2010.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014 Oct;80(2):162-7. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2014.06.007. Epub 2014 Jun 21. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 25053202
-
Use of daptomycin to treat infections with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates having vancomycin minimum inhibitory concentrations of 1.5 to 2 μg/mL.Ann Pharmacother. 2013 Dec;47(12):1654-65. doi: 10.1177/1060028013508272. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Ann Pharmacother. 2013. PMID: 24259618 Review.
-
Dysfunctional accessory gene regulator (agr) as a prognostic factor in invasive Staphylococcus aureus infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 26;10(1):20697. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-77729-0. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33244173 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Clinical and microbiological characteristics of persistent Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia, risk factors for mortality, and the role of CD4+ T cells.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 5;14(1):15472. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66520-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38969796 Free PMC article.
-
Genotypic Shift and Diversification of MRSA Blood Stream Isolates in a University Hospital Setting: Evidence from a 12-Year Observational Study.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Jul 19;13(7):670. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13070670. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061352 Free PMC article.
-
Global prevalence and distribution of vancomycin resistant, vancomycin intermediate and heterogeneously vancomycin intermediate Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 29;10(1):12689. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69058-z. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32728110 Free PMC article.
-
Vancomycin MIC and agr dysfunction in invasive MRSA infections in southern Brazil.Braz J Microbiol. 2020 Dec;51(4):1819-1823. doi: 10.1007/s42770-020-00384-0. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Braz J Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33074551 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Vancomycin MIC and Molecular Characteristics with Clinical Outcomes in Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus Acute Hematogenous Osteoarticular Infections in Children.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018 Apr 26;62(5):e00084-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00084-18. Print 2018 May. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018. PMID: 29530845 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Twenty third Informational supplement, M100-S23. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute; 2013.
-
- Appelbaum PC. Reduced glycopeptide susceptibility in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2007;30:398–408. - PubMed
-
- Zhuo C, Xu YC, Xiao SN, Zhang GY, Zhong NS. Glycopeptide minimum inhibitory concentration creep among meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from 2006-2011 in China. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2013;41:578–581. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical