Effects of fresh mineralized dentin and cementum on socket healing: a preliminary study in dogs
- PMID: 26131427
- PMCID: PMC4483524
- DOI: 10.5125/jkaoms.2015.41.3.119
Effects of fresh mineralized dentin and cementum on socket healing: a preliminary study in dogs
Abstract
Objectives: Dentin is composed of many minerals and growth factors. Based on this composition, we studied its effect as a possible regenerative material for alveolar healing.
Materials and methods: This study was conducted using four 2.5-year-old mongrel dogs (male; weight, 25 to 30 kg). The third mandibular premolars were carefully mobilized with a dental elevator and then removed using forceps. The crown portions of the extracted teeth were removed with cutters, and the root portions of the remaining teeth were collectively trimmed as closely as possible to 350 to 500 µm. Dentin and cementum (DC) chips harvested from the extracted teeth were soaked in blood and packed into the fresh sockets (autograft). Biopsies were performed at the ends of day 14 and day 56 following implantation. Data were expressed as mean±standard deviation and compared with t-test results.
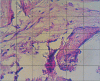
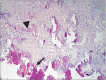
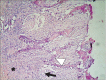
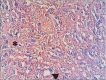
Results: The ratio of SA(bone) to total area of each probe was determined and was 170±16 µm(2) for the control group and 71±14 µm(2) for the DC group, a significant difference (P<0.05).
Conclusion: DC particulate grafts offered no improvement in bone regeneration in alveolar extraction sockets.
Keywords: Cementum; Dentin; Healing; Tooth extraction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Test in canine extraction site preservations by using mineralized collagen plug with or without membrane.J Biomater Appl. 2016 Apr;30(9):1285-99. doi: 10.1177/0885328215625429. Epub 2015 Dec 31. J Biomater Appl. 2016. PMID: 26721867
-
GTR treatment of degree III furcation defects following application of enamel matrix proteins. An experimental study in dogs.J Clin Periodontol. 1998 Jun;25(6):524-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1998.tb02482.x. J Clin Periodontol. 1998. PMID: 9667487
-
Healing of periodontal defects treated with enamel matrix proteins and root surface conditioning--an experimental study in dogs.Biomaterials. 2004 May;25(10):1831-40. doi: 10.1016/s0142-9612(03)00468-x. Biomaterials. 2004. PMID: 14738847
-
Healing of extraction sockets and surgically produced - augmented and non-augmented - defects in the alveolar ridge. An experimental study in the dog.J Clin Periodontol. 2005 May;32(5):435-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2005.00692.x. J Clin Periodontol. 2005. PMID: 15842256
-
Effect of enamel matrix proteins (Emdogain') on healing after re-implantation of "periodontally compromised" roots. An experimental study in the dog.J Clin Periodontol. 2003 Oct;30(10):855-61. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-051x.2003.00400.x. J Clin Periodontol. 2003. PMID: 14710765
Cited by
-
Demineralized dentin matrix scaffolds for alveolar bone engineering.J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2017 Apr-Jun;17(2):120-127. doi: 10.4103/jips.jips_62_17. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2017. PMID: 28584412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discussion: Effects of fresh mineralized dentin and cementum on socket healing: a preliminary study in dogs.J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015 Jun;41(3):124. doi: 10.5125/jkaoms.2015.41.3.124. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015. PMID: 26131428 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Stimulation of Osteogenic Activity of Autologous Teeth Hard Tissues as Bone Augmentation Material.Biology (Basel). 2024 Jan 11;13(1):40. doi: 10.3390/biology13010040. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38248471 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Different Bone Filling Materials and Resorbable Membranes by Means of Micro-Tomography. A Preliminary Study in Rabbits.Materials (Basel). 2019 Apr 12;12(8):1197. doi: 10.3390/ma12081197. Materials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31013766 Free PMC article.
-
Extraction socket sealing using palatal gingival grafts and resorbable collagen membranes.Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017 Dec 25;39(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s40902-017-0137-x. eCollection 2017 Dec. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017. PMID: 29302588 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Irinakis T. Rationale for socket preservation after extraction of a single-rooted tooth when planning for future implant placement. J Can Dent Assoc. 2006;72:917–922. - PubMed
-
- Botticelli D, Berglundh T, Lindhe J. Hard-tissue alterations following immediate implant placement in extraction sites. J Clin Periodontol. 2004;31:820–828. - PubMed
-
- Tan WL, Wong TL, Wong MC, Lang NP. A systematic review of post-extractional alveolar hard and soft tissue dimensional changes in humans. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012;23(Suppl 5):1–21. - PubMed
-
- Dimova C. Socket preservation procedure after tooth extraction. Key Engineering Materials. 2014;587:325–330.
-
- Vignoletti F, Matesanz P, Rodrigo D, Figuero E, Martin C, Sanz M. Surgical protocols for ridge preservation after tooth extraction. A systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012;23(Suppl 5):22–38. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

