The Impact of Diabetes Mellitus on Renal Cell Carcinoma Prognosis: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies
- PMID: 26131819
- PMCID: PMC4504607
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001055
The Impact of Diabetes Mellitus on Renal Cell Carcinoma Prognosis: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies
Abstract
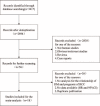
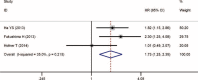
Previous studies that investigated the relationship between DM and survival in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) patients reported inconsistent findings. Hence, we conducted a meta-analysis to obtain a more precise evaluation of the prognostic significance of DM in RCC. A systematic review was conducted with PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science to identify relevant articles that evaluated the effect of DM on RCC patients. Based on the inclusion and quality assessment criteria, 18 studies were eligible for the meta-analysis. Pooled hazard ratios (HR) and corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI) for overall survival (OS), cancer-specific survival (CSS), and recurrence-free survival (RFS) were calculated by standard meta-analysis techniques. The results suggested that DM was associated with poor OS (HR 1.56, 95% CI, 1.35-1.81, P < 0.001), poor CSS (HR 2.03, 95% CI, 1.37-3.01, P < 0.001), and poor RFS (HR 1.73, 95% CI, 1.25-2.39, P = 0.012). In addition, for patients with localized RCC, patients with clear cell RCC, or patients receiving nephrectomy, DM was associated with both poor OS and CSS by subgroup analyses. Our study revealed that there was a significant negative impact of DM on OS, CSS, and RFS in RCC patients. Therefore, more attention should be paid to RCC patients with preexisting DM because of their poor prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Multi-institutional analysis of localized renal cell carcinoma that demonstrates the impact of diabetic status on prognosis after nephrectomy.Ann Surg Oncol. 2013 Oct;20(11):3662-8. doi: 10.1245/s10434-013-3147-7. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23907313
-
Prognostic nutritional index and prognosis in renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Urol Oncol. 2021 Oct;39(10):623-630. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2021.05.028. Epub 2021 Jul 10. Urol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34253447
-
Cancer stem cell markers predict a poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 4;7(40):65862-65875. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11672. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27588469 Free PMC article.
-
C-reactive protein is a predictor of prognosis in renal cell carcinoma patients receiving tyrosine kinase inhibitors: A meta-analysis.Clin Chim Acta. 2017 Dec;475:178-187. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2017.10.021. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Clin Chim Acta. 2017. PMID: 29080691
-
The association of platelet count with clinicopathological significance and prognosis in renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2015 May 8;10(5):e0125538. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125538. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25955026 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prevalence of diabetes and hospitalization due to poor glycemic control in people with bladder cancer or renal cell carcinoma in Sweden.BMC Urol. 2024 Jul 17;24(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s12894-024-01536-2. BMC Urol. 2024. PMID: 39020360 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic significance of preexisting diabetes in patients with surgically treated renal cell carcinoma: the ongoing debate.Ann Transl Med. 2019 Dec;7(Suppl 8):S321. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.09.131. Ann Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 32016039 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Preoperative serum total cholesterol is a predictor of prognosis in patients with renal cell carcinoma: a meta- analysis of observational studies.Int Braz J Urol. 2020 Mar-Apr;46(2):158-168. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2019.0560. Int Braz J Urol. 2020. PMID: 31961621 Free PMC article.
-
Primary and Immortalized Cultures of Human Proximal Tubule Cells Possess Both Progenitor and Non-Progenitor Cells That Can Impact Experimental Results.J Pers Med. 2023 Mar 31;13(4):613. doi: 10.3390/jpm13040613. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37108999 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of diabetes mellitus on oncological outcomes after radical hysterectomy for early stage cervical cancer.J Gynecol Oncol. 2016 May;27(3):e28. doi: 10.3802/jgo.2016.27.e28. J Gynecol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27029749 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ljungberg B. Prognostic markers in renal cell carcinoma. Curr Opin Urol 2007; 17:303–308. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R, DeSantis C, Virgo K, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 2012; 62:220–241. - PubMed
-
- Choi Y, Park B, Jeong BC, et al. Body mass index and survival in patients with renal cell carcinoma: a clinical-based cohort and meta-analysis. Int J Cancer 2013; 132:625–634. - PubMed
-
- Park YH, Lee JK, Kim KM, et al. Visceral obesity in predicting oncologic outcomes of localized renal cell carcinoma. J Urol 2014; 192:1043–1049. - PubMed

