Onychomycosis due to opportunistic molds
- PMID: 26131862
- PMCID: PMC4516115
- DOI: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20153521
Onychomycosis due to opportunistic molds
Abstract
Background: Onychomycosis are caused by dermatophytes and Candida, but rarely by non- dermatophyte molds. These opportunistic agents are filamentous fungi found as soil and plant pathogens.
Objectives: To determine the frequency of opportunistic molds in onychomycosis.
Methods: A retrospective analysis of 4,220 cases with onychomycosis, diagnosed in a 39-month period at the Institute of Dermatology and Skin surgery "Prof. Dr. Fernando A. Cordero C." in Guatemala City, and confirmed with a positive KOH test and culture.
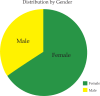
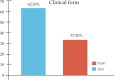
Results: 32 cases (0.76%) of onychomycosis caused by opportunistic molds were confirmed. The most affected age group ranged from 41 to 65 years (15 patients, 46.9%) and females were more commonly affected (21 cases, 65.6%) than males. Lateral and distal subungual onychomycosis (OSD-L) was detected in 20 cases (62.5%). The microscopic examination with KOH showed filaments in 19 cases (59.4%), dermatophytoma in 9 cases (28.1%), spores in 2 cases (6.25%), and filaments and spores in 2 cases (6.25%). Etiologic agents: Aspergillus sp., 11 cases (34.4%); Scopulariopsis brevicaulis, 8 cases (25.0%); Cladosporium sp., 3 cases (9.4%); Acremonium sp., 2 cases (6.25%); Paecilomyces sp., 2 cases (6.25%); Tritirachium oryzae, 2 cases (6.25%); Fusarium sp., Phialophora sp., Rhizopus sp. and Alternaria alternate, 1 case (3.1%) each.
Conclusions: We found onychomycosis by opportunistic molds in 0.76% of the cases and DLSO was present in 62.5%. The most frequent isolated etiological agents were: Aspergillus sp. and Scopulariopsis brevicaulis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None.
Figures
References
-
- López-Jodra O, Torres-Rodriguez J. Especies fúngicas poco comunes responsables de onicomicosis. Rev Iberoam Micol. 1999;16:S11–S15. - PubMed
-
- Crespo V, Delgado V. Erchiga VC, Florencio VD. Atlas de Micología Cutánea. Madrid, España: Loky & Dimas; 2006. Micosis ungueales; pp. 9–11.
-
- Asbati M, Smythe B, Cavallera E. Onicomicosis por hongos no dematofitos. Estudio retrospectivo en 4 años. Rev Soc Ven Microbiol. 2002;22:147–152.
-
- Araujo AJG, Bastos OMP, Souza MAJ, Oliveira JC. Onychomycosis caused by emergent fungi:clinical analysis, diagnosis and revisión. An Bras Dermatol. 2003;78:445–455.
-
- Salas I, Chavez O. Agentes de Onicomicosis en Costa Rica. Rev Costarric Cienc Méd. 2004;25:43–47.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical