Discovery and Fine-Mapping of Glycaemic and Obesity-Related Trait Loci Using High-Density Imputation
- PMID: 26132169
- PMCID: PMC4488845
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005230
Discovery and Fine-Mapping of Glycaemic and Obesity-Related Trait Loci Using High-Density Imputation
Abstract
Reference panels from the 1000 Genomes (1000G) Project Consortium provide near complete coverage of common and low-frequency genetic variation with minor allele frequency ≥0.5% across European ancestry populations. Within the European Network for Genetic and Genomic Epidemiology (ENGAGE) Consortium, we have undertaken the first large-scale meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies (GWAS), supplemented by 1000G imputation, for four quantitative glycaemic and obesity-related traits, in up to 87,048 individuals of European ancestry. We identified two loci for body mass index (BMI) at genome-wide significance, and two for fasting glucose (FG), none of which has been previously reported in larger meta-analysis efforts to combine GWAS of European ancestry. Through conditional analysis, we also detected multiple distinct signals of association mapping to established loci for waist-hip ratio adjusted for BMI (RSPO3) and FG (GCK and G6PC2). The index variant for one association signal at the G6PC2 locus is a low-frequency coding allele, H177Y, which has recently been demonstrated to have a functional role in glucose regulation. Fine-mapping analyses revealed that the non-coding variants most likely to drive association signals at established and novel loci were enriched for overlap with enhancer elements, which for FG mapped to promoter and transcription factor binding sites in pancreatic islets, in particular. Our study demonstrates that 1000G imputation and genetic fine-mapping of common and low-frequency variant association signals at GWAS loci, integrated with genomic annotation in relevant tissues, can provide insight into the functional and regulatory mechanisms through which their effects on glycaemic and obesity-related traits are mediated.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal's policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: GT, VSt, UT, and KS are employed by deCODE Genetics/Amgen inc. This does not alter our adherence to all PLOS policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
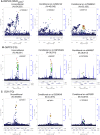
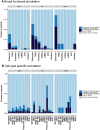
References
-
- Rose KM, Newman B, Mayer-Davis EJ, Selby JV (1998) Genetic and behavioural determinants of waist-hip ratio and waist circumference in women twins. Obes Res 6: 383–392. - PubMed
-
- Poulsen P, Kyvik KO, Vaag A, Beck-Nielsen H (1999) Heritability of type II (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus and abnormal glucose tolerance—a population-based twin study. Diabetologia 42: 139–145. - PubMed
-
- Poulsen P, Levin K, Petersen I, Christensen K, Beck-Nielsen H, et al. (2005) Heritability of insulin secretion, peripheral and hepatic insulin action, and intracellular glucose partitioning in young and old Danish twins. Diabetes 54: 275–283. - PubMed
-
- Silventoinen K, Rokholm B, Kaprio J, Sørensen TI (2010) The genetic and environmental influences on childhood obesity: a systematic review of twin and adoption studies. Int J Obes 34: 29–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RC2 MH089951/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH081802/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087679/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 MH089995/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- AA-09203/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- 1RL1MH083268-01/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- AA-00145/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA15416/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01HL087679/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1RC2 MH089995-01/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K05 AA000145/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA-12502/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- 098381/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- WT064890/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- K02AA018755/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- G1001799/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 098017/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- WT090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- GR069224/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 1RC2MH089951-01/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA009203/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/N01104X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 DK062418/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K02 AA018755/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01D0042157-01A/PHS HHS/United States
- U24 MH068457/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G0500539/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AA012502/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 MH068457-06/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA015416/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- RL1 MH083268/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G0902313/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0600705/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R37 AA012502/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- MH081802/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

