Detection of influenza B lineages from 2001 to 2013 in a tertiary hospital in the city of São Paulo, Brazil
- PMID: 26132429
- PMCID: PMC4569822
- DOI: 10.1590/0074-02760150044
Detection of influenza B lineages from 2001 to 2013 in a tertiary hospital in the city of São Paulo, Brazil
Abstract
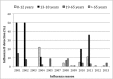
Two antigenically distinct lineages of influenza B viruses, the Victoria-like and Yamagata-like strains, currently circulate among humans. Surveillance from United States of America and Europe over the last 10 years showed that the chance of a correct matching between vaccine and the circulating lineage had been 50%. We investigated influenza B infection in different patient groups (asymptomatic, general community, with comorbidities and hospitalised) attended at a tertiary hospital in the city of São Paulo, Brazil between 2001-2013. All samples were screened for influenza B virus by one-step real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. From 2,992 respiratory samples collected, 114 (3.8%) tested positive for influenza B. Teenagers (13-18 years) presented the highest rate of 18.5% (odds ratio 22.87, 95% confidence interval 2.90-180.66, p < 0.001). One hundred nine samples could be characterised: 50 were Yamagata-like and 59 were Victoria-like strains. Mismatching between the vaccine and predominant circulating strain was observed in 2002 and 2013 seasons. Based on data collected during a period of 12 years, we found that influenza B was more frequent in teenagers. Co-circulation of both lineages and mismatch with the vaccine strain can occur. Our data highlighted the importance of quadrivalent vaccines and future analysis of the age groups included in vaccination programs.
Figures
References
-
- CDC - Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Influenza activity - United States and worldwide, 2007-08 season. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2008;57:692–697. - PubMed
-
- CDC - Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC protocol of real-time RT-PCR for influenza A(H1N1) 2009. http://who.int/csr/resources/publications/swineflu/CDCRealtimeRTPCR_Swin....
-
- Chan PK, Chan MC, Cheung JL, Lee N, Leung TF, Yeung ACM, Wong MCS, Ngai KL, Nelson EAS, Hui DS. Influenza B lineage circulation and hospitalization rates in a subtropical city, Hong Kong, 2000-2010. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;56:677–684. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical