IL-13 Stimulates Proliferation and Expression of Mucin and Immunomodulatory Genes in Cultured Conjunctival Goblet Cells
- PMID: 26132778
- PMCID: PMC4495812
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.14-15496
IL-13 Stimulates Proliferation and Expression of Mucin and Immunomodulatory Genes in Cultured Conjunctival Goblet Cells
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the effects of IL-13 on goblet cell proliferation, differentiation, and expression of mucin and immunomodulatory genes.
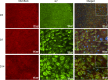
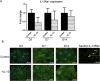
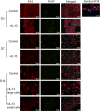
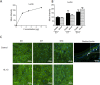
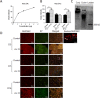
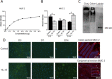
Methods: Explants were excised from the conjunctiva of young C57BL/6 mice. Cultures received 200 μL per week of either Keratinocyte media (KSFM) or KSFM supplemented with 10 ng/mL IL-13 and were incubated for 3 (D3), 7 (D7), or 14 (D14) days. Subsequently, cell proliferation was assessed or cultures were immunostained, collected for dot blot, or for reverse transcription (RT) and quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) or for RT-PCR gene array.
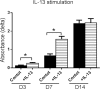
Results: The cultured conjunctival epithelium expressed goblet cell associated keratin 7 and mucins MUC5AC and MUC2 and when stimulated with IL-13 showed increased proliferation at D3 and D7 (P < 0.05) compared with control. MUC5AC expression was increased in the IL-13-treated group at D3 and D14 (P < 0.05). IL-13-treated cultures showed increased chemokine ligand 26 (CCL26), chloride channel calcium activated channel 3 (CLCA3), fas ligand (FasL), and Relm-β at D7. All conjunctival cultures expressed MUC2, and its expression was decreased at D3 (P < 0.05) and increased at D14 (P < 0.05) with IL-13 treatment.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated that conjunctival goblet cells are IL-13 responsive cells that produce factors known to maintain epithelial barrier, stimulate mucin production, and modulate immune response in nonocular mucosa when treated with IL-13. The functional significance of IL-13-stimulated factors remains to be determined.
Figures


References
-
- Watsky MA,, Jablonski MM,, Edelhauser HF. Comparison of conjunctival and corneal surface areas in rabbit and human. Curr Eye Res. 1988; 7: 483–486. - PubMed
-
- Gipson IK. Distribution of mucins at the ocular surface. Exp Eye Res. 2004; 78: 379–388. - PubMed
-
- Pflugfelder SC,, Tseng SCG,, Yoshino K,, Monroy D,, Felix C,, Reis BL. Correlation of goblet cell density and mucosal epithelial membrane mucin expression with rose bengal staining in patients with ocular irritation. Ophthalmology. 1997; 104: 223–235. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

