Magnetically Targeted Stem Cell Delivery for Regenerative Medicine
- PMID: 26133387
- PMCID: PMC4598669
- DOI: 10.3390/jfb6030526
Magnetically Targeted Stem Cell Delivery for Regenerative Medicine
Abstract
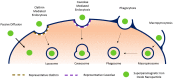
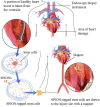
Stem cells play a special role in the body as agents of self-renewal and auto-reparation for tissues and organs. Stem cell therapies represent a promising alternative strategy to regenerate damaged tissue when natural repairing and conventional pharmacological intervention fail to do so. A fundamental impediment for the evolution of stem cell therapies has been the difficulty of effectively targeting administered stem cells to the disease foci. Biocompatible magnetically responsive nanoparticles are being utilized for the targeted delivery of stem cells in order to enhance their retention in the desired treatment site. This noninvasive treatment-localization strategy has shown promising results and has the potential to mitigate the problem of poor long-term stem cell engraftment in a number of organ systems post-delivery. In addition, these same nanoparticles can be used to track and monitor the cells in vivo, using magnetic resonance imaging. In the present review we underline the principles of magnetic targeting for stem cell delivery, with a look at the logic behind magnetic nanoparticle systems, their manufacturing and design variants, and their applications in various pathological models.
Keywords: SPION; magnetic nanoparticle; magnetic targeting; regenerative medicine; stem cell.
Figures
References
-
- Rudolph K. Adult Stem Cells in Aging, Diseases, and Cancer. Karger AG; Basel, Switzerland: 2015.
-
- Stem Cell Information. National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Website. [(accessed on 5 June 2015)]; Available online: http://stemcells.nih.gov/info/basics/pages/basics1.aspx.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources