Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Lipophilic 1,4-Naphthoquinone Derivatives against Human Cancer Cell Lines
- PMID: 26133763
- PMCID: PMC6331847
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules200711994
Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Lipophilic 1,4-Naphthoquinone Derivatives against Human Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
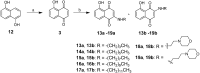
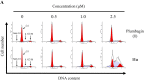
To examine the effect of hydrophobicity on the anticancer activity of 1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives, a series of compounds bearing a 2-O-alkyl-, 3-C-alkyl- or 2/3-N-morpholinoalkyl group were synthesized and evaluated for their anticancer activity against five human cancer cell lines in vitro. The cytotoxicity of these derivatives was assayed against HT-29, SW480, HepG2, MCF-7 and HL-60 cells by the MTT assay. Among them, 2-hydroxy-3-farnesyl-1,4-naphthoquinone (11a) was found to be the most cytotoxic against these cell lines. Our results showed that the effectiveness of compound 11a may be attributed to its suppression of the survival of HT-29. Secondly, in the Hoechst 33258 staining test, compound 11a-treated cells exhibited nuclear condensation typical of apoptosis. Additionally, cell cycle analysis by flow cytometry indicated that compound 11a arrested HT-29 cells in the S phase. Furthermore, cell death detected by Annexin V-FITC/propidium iodide staining showed that compound 11a efficiently induced apoptosis of HT-29 in a concentration-dependent manner. Taken together, compound 11a effectively inhibits colon cancer cell proliferation and may be a potent anticancer agent.
Keywords: 1,4-naphthoquinone; anticancer activity; apoptosis; cell cycle distribution; human colon cancer cells HT-29; terpenoids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
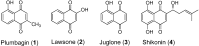





Similar articles
-
Cytotoxicity of Synthesized 1,4-Naphthoquinone Oxime Derivatives on Selected Human Cancer Cell Lines.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2018;66(6):612-619. doi: 10.1248/cpb.c18-00013. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2018. PMID: 29863062
-
Synthesis and anticancer activity of some novel 5,6-fused hybrids of juglone based 1,4-naphthoquinones.Eur J Med Chem. 2014 Aug 18;83:84-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.06.012. Epub 2014 Jun 10. Eur J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24953027
-
Cytotoxicity of synthesized 1,4-naphthoquinone analogues on selected human cancer cell lines.Bioorg Med Chem. 2014 Sep 1;22(17):5013-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2014.06.013. Epub 2014 Jul 4. Bioorg Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 25059501
-
Synthesis, characterization and antiproliferative activity of 1,2-naphthoquinone and its derivatives.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2012 Jul;167(5):1430-45. doi: 10.1007/s12010-012-9551-9. Epub 2012 Jan 19. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22258648
-
Anti-cancer Research on Arnebiae radix-derived Naphthoquinone in Recent Five Years.Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2022;17(3):218-230. doi: 10.2174/1574892816666211209164745. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2022. PMID: 34886780 Review.
Cited by
-
Biosynthesis and molecular actions of specialized 1,4-naphthoquinone natural products produced by horticultural plants.Hortic Res. 2016 Sep 21;3:16046. doi: 10.1038/hortres.2016.46. eCollection 2016. Hortic Res. 2016. PMID: 27688890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological Activity of Naphthoquinones Derivatives in the Search of Anticancer Lead Compounds.Toxins (Basel). 2023 May 20;15(5):348. doi: 10.3390/toxins15050348. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37235382 Free PMC article.
-
The diverse mechanisms and anticancer potential of naphthoquinones.Cancer Cell Int. 2019 Aug 2;19:207. doi: 10.1186/s12935-019-0925-8. eCollection 2019. Cancer Cell Int. 2019. PMID: 31388334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ionically Crosslinked Chitosan Membranes Used as Drug Carriers for Cancer Therapy Application.Materials (Basel). 2018 Oct 20;11(10):2051. doi: 10.3390/ma11102051. Materials (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30347857 Free PMC article.
-
The evaluation of in vitro antichagasic and anti-SARS-CoV-2 potential of inclusion complexes of β- and methyl-β-cyclodextrin with naphthoquinone.J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2023 Mar;81:104229. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2023.104229. Epub 2023 Feb 8. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 36776572 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO Report. [(accessed on 25 June 2015)]. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs297/en/index.html.
-
- Prasad K.R., Babu K.S., Rao R.R., Suresh G., Rekha K., Murthy J.M., Rani P.U., Rao J.M. Synthesis and insect antifeedant activity of plumbagin derivatives. Med. Chem. Res. 2012;21:578–583. doi: 10.1007/s00044-011-9559-7. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

