pigk Mutation underlies macho behavior and affects Rohon-Beard cell excitability
- PMID: 26133798
- PMCID: PMC4541141
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00355.2015
pigk Mutation underlies macho behavior and affects Rohon-Beard cell excitability
Abstract
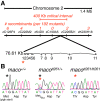
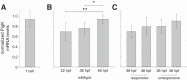
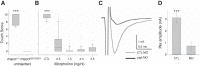
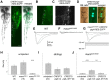
The study of touch-evoked behavior allows investigation of both the cells and circuits that generate a response to tactile stimulation. We investigate a touch-insensitive zebrafish mutant, macho (maco), previously shown to have reduced sodium current amplitude and lack of action potential firing in sensory neurons. In the genomes of mutant but not wild-type embryos, we identify a mutation in the pigk gene. The encoded protein, PigK, functions in attachment of glycophosphatidylinositol anchors to precursor proteins. In wild-type embryos, pigk mRNA is present at times when mutant embryos display behavioral phenotypes. Consistent with the predicted loss of function induced by the mutation, knock-down of PigK phenocopies maco touch insensitivity and leads to reduced sodium current (INa) amplitudes in sensory neurons. We further test whether the genetic defect in pigk underlies the maco phenotype by overexpressing wild-type pigk in mutant embryos. We find that ubiquitous expression of wild-type pigk rescues the touch response in maco mutants. In addition, for maco mutants, expression of wild-type pigk restricted to sensory neurons rescues sodium current amplitudes and action potential firing in sensory neurons. However, expression of wild-type pigk limited to sensory cells of mutant embryos does not allow rescue of the behavioral touch response. Our results demonstrate an essential role for pigk in generation of the touch response beyond that required for maintenance of proper INa density and action potential firing in sensory neurons.
Keywords: Nav; Pigk; Rohon-Beard cells; glycophosphatidylinositol-anchored protein; touch response.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Almeida AM, Murakami Y, Layton DM, Hillmen P, Sellick GS, Maeda Y, Richards S, Patterson S, Kotsianidis I, Mollica L, Crawford DH, Baker A, Ferguson M, Roberts I, Houlston R, Kinoshita T, Karadimitris A. Hypomorphic promoter mutation in PIGM causes inherited glycosylphosphatidylinositol deficiency. Nat Med 12: 846–851, 2006. - PubMed
-
- Amores A, Force A, Yan YL, Joly L, Amemiya C, Fritz A, Ho RK, Langeland J, Prince V, Wang YL, Westerfield M, Ekker M, Postlethwait JH. Zebrafish hox clusters and vertebrate genome evolution. Science 282: 1711–1714, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Bernhardt RR, Chitnis AB, Lindamer L, Kuwada JY. Identification of spinal neurons in the embryonic and larval zebrafish. J Comp Neurol 302: 603–616, 1990. - PubMed
-
- Casadei R, Pelleri MC, Vitale L, Facchin F, Lenzi L, Canaider S, Strippoli P, Frabetti F. Identification of housekeeping genes suitable for gene expression analysis in the zebrafish. Gene Express Patterns 11: 271–276, 2011. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

