Effect of N-n-butyl haloperidol iodide on ROS/JNK/Egr-1 signaling in H9c2 cells after hypoxia/reoxygenation
- PMID: 26134032
- PMCID: PMC4488875
- DOI: 10.1038/srep11809
Effect of N-n-butyl haloperidol iodide on ROS/JNK/Egr-1 signaling in H9c2 cells after hypoxia/reoxygenation
Abstract
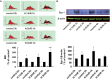
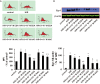
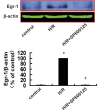
Reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced oxidative stress in cells is an important pathophysiological process during myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury, and the transcription factor Egr-1 is a master switch for various damage pathways during reperfusion injury. An in vitro model of myocardial I/R injury and H9c2 cardiomyoblast cells hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) was used to assess whether there is abnormal intracellular ROS/JNK/Egr-1 signaling. We also assessed whether N-n-butyl haloperidol (F2), which exerts protective effects during myocardial I/R injury, can modulate this pathway. H/R induced ROS generation, JNK activation, and increased the expression of Egr-1 protein in H9c2 cells. The ROS scavengers edaravone (EDA) and N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) reduced ROS level, downregulated JNK activation, and Egr-1 expression in H9c2 cells after H/R. The JNK inhibitor SP600125 inhibited Egr-1 overexpression in H9c2 cells caused by H/R. F2 could downregulate H/R-induced ROS level, JNK activation, and Egr-1 expression in H9c2 cells in a dose-dependent manner. The ROS donor hypoxanthine-xanthine oxidase (XO/HX) and the JNK activator ANISO antagonized the effects of F2. Therefore, H/R activates ROS/Egr-1 signaling pathway in H9c2 cells, and JNK activation plays an important role in this pathway. F2 regulates H/R-induced ROS/JNK/Egr-1 signaling, which might be an important mechanism by which it antagonizes myocardial I/R injury.
Figures




Similar articles
-
N-n-butyl Haloperidol Iodide Protects against Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury in Cardiac Microvascular Endothelial Cells by Regulating the ROS/MAPK/Egr-1 Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Jan 5;7:520. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00520. eCollection 2016. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28111550 Free PMC article.
-
N-n-Butyl Haloperidol Iodide Ameliorates Oxidative Stress in Mitochondria Induced by Hypoxia/Reoxygenation through the Mitochondrial c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase/Sab/Src/Reactive Oxygen Species Pathway in H9c2 Cells.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 May 8;2019:7417561. doi: 10.1155/2019/7417561. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31205589 Free PMC article.
-
N-n-Butyl Haloperidol Iodide, a Derivative of the Anti-psychotic Haloperidol, Antagonizes Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury by Inhibiting an Egr-1/ROS Positive Feedback Loop in H9c2 Cells.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Jan 25;9:19. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00019. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29422863 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive species mechanisms of cellular hypoxia-reoxygenation injury.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002 Feb;282(2):C227-41. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00112.2001. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11788333 Review.
-
Reactive oxygen species in myocardial reperfusion injury: from physiopathology to therapeutic approaches.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012 Jan;13(1):97-114. doi: 10.2174/138920112798868782. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 21470157 Review.
Cited by
-
Early Growth Response 1 Contributes to Renal IR Injury by Inducing Proximal Tubular Cell Apoptosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 19;24(18):14295. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814295. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762598 Free PMC article.
-
The c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway is activated in human interstitial cystitis (IC) and rat protamine sulfate induced cystitis.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 17;6:19670. doi: 10.1038/srep19670. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26883396 Free PMC article.
-
N-n-butyl Haloperidol Iodide Protects against Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury in Cardiac Microvascular Endothelial Cells by Regulating the ROS/MAPK/Egr-1 Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Jan 5;7:520. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00520. eCollection 2016. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28111550 Free PMC article.
-
JNK-dependent phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of EGR-1 promotes cardiomyocyte apoptosis.Apoptosis. 2022 Apr;27(3-4):246-260. doi: 10.1007/s10495-022-01714-3. Epub 2022 Feb 1. Apoptosis. 2022. PMID: 35103892
-
Emodin protects against oxidative stress and apoptosis in HK-2 renal tubular epithelial cells after hypoxia/reoxygenation.Exp Ther Med. 2017 Jul;14(1):447-452. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4473. Epub 2017 May 18. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 28672952 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Minamino T. Cardioprotection from ischemia/reperfusion injury: basic and translational research. Circ J. 76, 1074–1082 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

