Thymoquinone inhibits TNF-α-induced inflammation and cell adhesion in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts by ASK1 regulation
- PMID: 26134265
- PMCID: PMC4549173
- DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2015.06.017
Thymoquinone inhibits TNF-α-induced inflammation and cell adhesion in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts by ASK1 regulation
Abstract
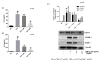
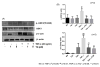
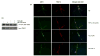
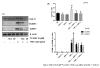
Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) is a pro-inflammatory cytokine produced by monocytes/macrophage that plays a pathological role in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In this study, we investigate the effect of thymoquinone (TQ), a phytochemical found in Nigella sativa, in regulating TNF-α-induced RA synovial fibroblast (RA-FLS) activation. Treatment with TQ (1-5μM) had no marked effect on the viability of human RA-FLS. Pre-treatment of TQ inhibited TNF-α-induced interleukin-6 (IL-6) and IL-8 production and ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and cadherin-11 (Cad-11) expression in RA-FLS (p<0.01). Evaluation of the signaling events showed that TQ inhibited TNF-α-induced phospho-p38 and phospho-JNK expression, but had no inhibitory effect on NF-κB pathway, in RA-FLS (p<0.05; n=4). Interestingly, we observed that selective down-regulation of TNF-α-induced phospho-p38 and phospho-JNK activation by TQ is elicited through inhibition of apoptosis-regulated signaling kinase 1 (ASK1). Furthermore, TNF-α selectively induced phosphorylation of ASK1 at Thr845 residue in RA-FLS, which was inhibited by TQ pretreatment in a dose dependent manner (p<0.01). Pre-treatment of RA-FLS with ASK1 inhibitor (TC ASK10), blocked TNF-α induced expression of ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and Cad-11. Our results suggest that TNF-α-induced ASK1-p38/JNK pathway is an important mediator of cytokine synthesis and enhanced expression of adhesion molecule in RA-FLS and TQ, by selectively inhibiting this pathway, may have a potential therapeutic value in regulating tissue destruction observed in RA.
Keywords: ASK1; MAP kinase; Rheumatoid arthritis; Synovial fibroblasts; TNF-α; Thymoquinone.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
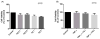
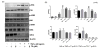
Similar articles
-
Anti-inflammatory activities of Chinese herbal medicine sinomenine and Liang Miao San on tumor necrosis factor-α-activated human fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Sep 1;137(1):457-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.05.048. Epub 2011 Jun 6. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21679760
-
Resveratrol inhibits TNF-α-induced IL-1β, MMP-3 production in human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes via modulation of PI3kinase/Akt pathway.Rheumatol Int. 2013 Jul;33(7):1829-35. doi: 10.1007/s00296-012-2657-0. Epub 2013 Jan 18. Rheumatol Int. 2013. PMID: 23328930
-
Gastrodia elata attenuates inflammatory response by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Jan;85:177-181. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.11.136. Epub 2016 Dec 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 27936399
-
[Rheumatoid arthritis: new developments in the pathogenesis with special reference to synovial fibroblasts].Z Rheumatol. 2001 Oct;60(5):309-18. doi: 10.1007/s003930170030. Z Rheumatol. 2001. PMID: 11759230 Review. German.
-
Macrophage polarization in rheumatoid arthritis: signaling pathways, metabolic reprogramming, and crosstalk with synovial fibroblasts.Front Immunol. 2024 May 10;15:1394108. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1394108. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38799455 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Thymoquinone (TQ) Inhibits Inflammation and Migration of THP-1 Macrophages: Mechanistic Insights into the Prevention of Atherosclerosis Using In-Vitro and In-Silico Analysis.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022 Apr 15;44(4):1740-1753. doi: 10.3390/cimb44040120. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35723378 Free PMC article.
-
A novel diindolylmethane analog, 1,1-bis(3'-indolyl)-1-(p-chlorophenyl) methane, inhibits the tumor necrosis factor-induced inflammatory response in primary murine synovial fibroblasts through a Nurr1-dependent mechanism.Mol Immunol. 2018 Sep;101:46-54. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2018.05.024. Epub 2018 Jun 2. Mol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29870816 Free PMC article.
-
Rituximab exerts its anti-arthritic effects via inhibiting NF-κB/GM-CSF/iNOS signaling in B cells in a mouse model of collagen-induced arthritis.Heliyon. 2023 May 25;9(6):e16673. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16673. eCollection 2023 Jun. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37274671 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Findings on Thymoquinone and Its Applications as a Nanocarrier for the Treatment of Cancer and Rheumatoid Arthritis.Pharmaceutics. 2021 May 22;13(6):775. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13060775. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34067322 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nigella sativa oil mitigates xerostomia and preserves salivary function in radiotherapy-treated mice.Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2023 Jul 25;8(4):912-920. doi: 10.1002/lio2.1122. eCollection 2023 Aug. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 37621284 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdel-Aziz H, Wadie W, Abdallah DM, Lentzen G, Khayyal MT. Novel effects of ectoine, a bacteria-derived natural tetrahydropyrimidine, in experimental colitis. Phytomedicine. 2013;20:585–591. - PubMed
-
- Adiseshaiah P, Kalvakolanu DV, Reddy SP. A JNK-independent signaling pathway regulates TNF alpha-stimulated, c-Jun-driven FRA-1 protooncogene transcription in pulmonary epithelial cells. J Immunol. 2006;177:7193–7202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

