microRNAs as Developmental Regulators
- PMID: 26134312
- PMCID: PMC4484971
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a008144
microRNAs as Developmental Regulators
Abstract
The field of miRNA biology is relatively young, but its impact on our understanding of the regulation of a wide array of cell functions is far-reaching. The importance of miRNAs in development has become nearly ubiquitous, with miRNAs contributing to development of most cells and organs. Although miRNAs are clearly interwoven into known regulatory networks that control cell development, the specific modalities by which they intersect are often quite distinct and cleverly achieved. The frequently emerging theme of feed-back and feed-forward loops to either counterbalance or reinforce the gene programs that they influence is a common thread. Many of these examples of miRNAs as developmental regulators are presently found in organs with different miRNAs and targets, whereas novel, unexpected themes emerge in the context of mouse development as we learn more about this rapidly developing area of biology.
Copyright © 2015 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures
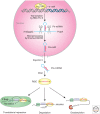
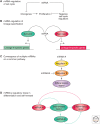
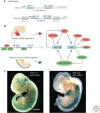
References
-
- Borchert GM, Lanier W, Davidson BL. 2006. RNA polymerase III transcribes human microRNAs. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13: 1097–1101. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhuri K, Chatterjee R. 2007. MicroRNA detection and target prediction: Integration of computational and experimental approaches. DNA Cell Biol 26: 321–337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
