Significance of filamin A in mTORC2 function in glioblastoma
- PMID: 26134617
- PMCID: PMC4489161
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-015-0396-z
Significance of filamin A in mTORC2 function in glioblastoma
Abstract
Background: Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is one of the most highly metastatic cancers. GBM has been associated with a high level of the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 2 (mTORC2) activity. We aimed to observe roles of mTORC2 in GBM cells especially on actin cytoskeleton reorganization, cell migration and invasion, and further determine new important players involved in the regulation of these cellular processes.
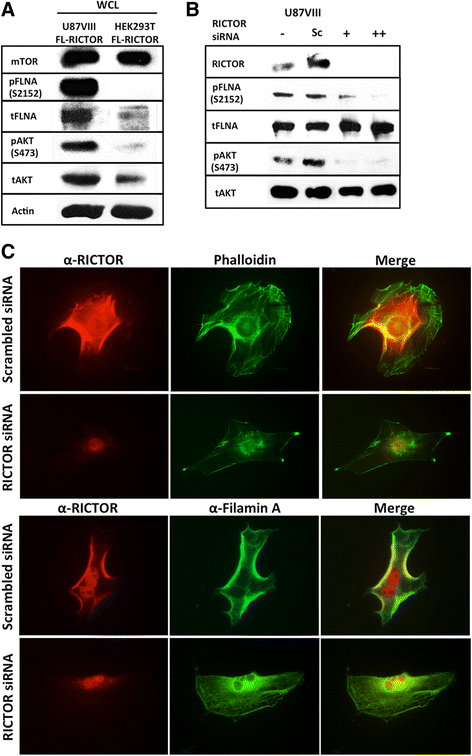
Methods: To further investigate the significance of mTORC2 in GBM, we treated GBM cells with PP242, an ATP-competitive inhibitor of mTOR, and used RICTOR siRNA to knock down mTORC2 activity. Effects on actin cytoskeleton, focal adhesion, migration, and invasion of GBM cells were examined. To gain insight into molecular basis of the mTORC2 effects on cellular cytoskeletal arrangement and motility/invasion, we affinity purified mTORC2 from GBM cells and identified proteins of interest by mass spectrometry. Characterization of the protein of interest was performed.
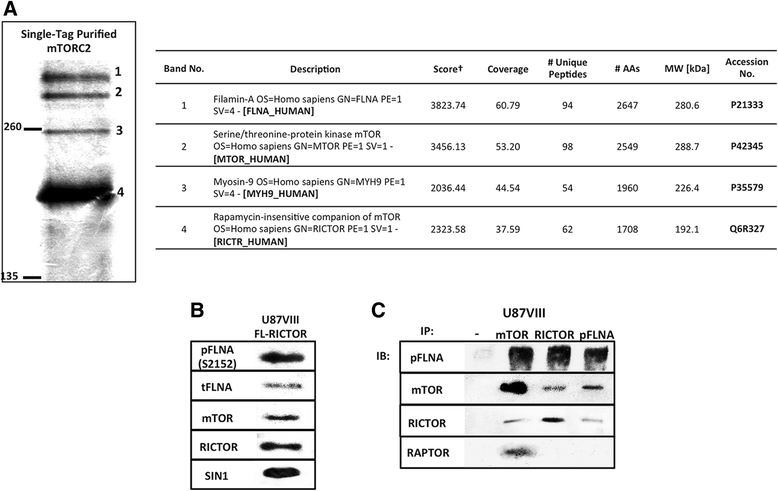
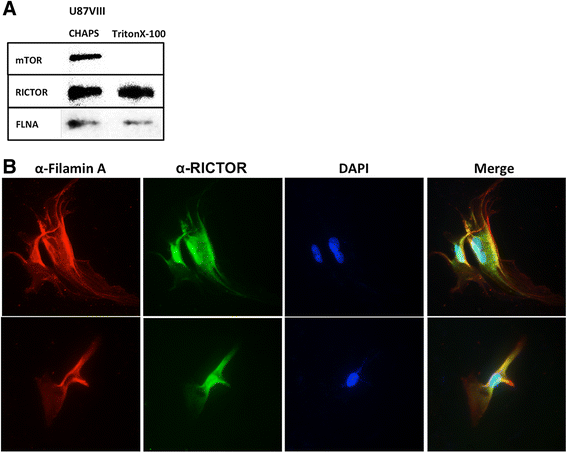
Results: In addition to the inhibition of mTORC2 activity, we demonstrated significant alteration of actin distribution as revealed by the use of phalloidin staining. Furthermore, vinculin staining was altered which suggests changes in focal adhesion. Inhibition of cell migration and invasion was observed with PP242. Two major proteins that are associated with this mTORC2 multiprotein complex were found. Mass spectrometry identified one of them as Filamin A (FLNA). Association of FLNA with RICTOR but not mTOR was demonstrated. Moreover, in vitro, purified mTORC2 can phosphorylate FLNA likewise its known substrate, AKT. In GBM cells, colocalization of FLNA with RICTOR was observed, and the overall amounts of FLNA protein as well as phosphorylated FLNA are high. Upon treatments of RICTOR siRNA or PP242, phosphorylated FLNA levels at the regulatory residue (Ser2152) decreased. This treatment also disrupted colocalization of Actin filaments and FLNA.
Conclusions: Our results support FLNA as a new downstream effector of mTORC2 controlling GBM cell motility. This new mTORC2-FLNA signaling pathway plays important roles in motility and invasion of glioblastoma cells.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Specific blockade of Rictor-mTOR association inhibits mTORC2 activity and is cytotoxic in glioblastoma.PLoS One. 2017 Apr 28;12(4):e0176599. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176599. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2023 Sep 8;18(9):e0291490. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291490. PMID: 28453552 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
ATP-site binding inhibitor effectively targets mTORC1 and mTORC2 complexes in glioblastoma.Int J Oncol. 2016 Mar;48(3):1045-52. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3311. Epub 2015 Dec 28. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26719046
-
Involvement of mTORC1 and mTORC2 in regulation of glioblastoma multiforme growth and motility.Int J Oncol. 2009 Oct;35(4):731-40. doi: 10.3892/ijo_00000386. Int J Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19724909
-
mTOR-Rictor-EGFR axis in oncogenesis and diagnosis of glioblastoma multiforme.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 May;48(5):4813-4835. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06462-2. Epub 2021 Jun 16. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34132942 Review.
-
Discrete signaling mechanisms of mTORC1 and mTORC2: Connected yet apart in cellular and molecular aspects.Adv Biol Regul. 2017 May;64:39-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2016.12.001. Epub 2017 Jan 4. Adv Biol Regul. 2017. PMID: 28189457 Review.
Cited by
-
The Host Scaffolding Protein Filamin A and the Exocyst Complex Control Exocytosis during InlB-Mediated Entry of Listeria monocytogenes.Infect Immun. 2018 Dec 19;87(1):e00689-18. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00689-18. Print 2019 Jan. Infect Immun. 2018. PMID: 30348826 Free PMC article.
-
Calpain suppresses cell growth and invasion of glioblastoma multiforme by producing the cleavage of filamin A.Int J Clin Oncol. 2020 Jun;25(6):1055-1066. doi: 10.1007/s10147-020-01636-7. Epub 2020 Feb 27. Int J Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32103382
-
Suppression of the invasive potential of Glioblastoma cells by mTOR inhibitors involves modulation of NFκB and PKC-α signaling.Sci Rep. 2016 Mar 4;6:22455. doi: 10.1038/srep22455. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26940200 Free PMC article.
-
Hedgehog signaling regulates the development and treatment of glioblastoma.Oncol Lett. 2022 Jul 5;24(3):294. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13414. eCollection 2022 Sep. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35949611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clonal Evolution of a High-Grade Pediatric Glioma With Distant Metastatic Spread.Neurol Genet. 2021 Feb 15;7(2):e561. doi: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000561. eCollection 2021 Apr. Neurol Genet. 2021. PMID: 33898738 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tanaka K, Babic I, Nathanson D, Akhavan D, Guo D, Gini B, et al. Oncogenic EGFR signaling activates an mTORC2-NF-κB pathway that promotes chemotherapy resistance. Cancer Discov. 2011;1:524–38. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0124. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

