Etomidate Impairs Long-Term Potentiation In Vitro by Targeting α5-Subunit Containing GABAA Receptors on Nonpyramidal Cells
- PMID: 26134653
- PMCID: PMC4571505
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0315-15.2015
Etomidate Impairs Long-Term Potentiation In Vitro by Targeting α5-Subunit Containing GABAA Receptors on Nonpyramidal Cells
Abstract
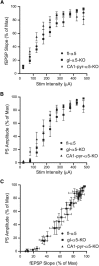
Previous experiments using genetic and pharmacological manipulations have provided strong evidence that etomidate impairs synaptic plasticity and memory by modulating α5-subunit containing GABAA receptors (α5-GABAARs). Because α5-GABAARs mediate tonic inhibition (TI) in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells and etomidate enhances TI, etomidate enhancement of TI in pyramidal cells has been proposed as the underlying mechanism (Martin et al., 2009). Here we tested this hypothesis by selectively removing α5-GABAARs from pyramidal neurons (CA1-pyr-α5-KO) and comparing the ability of etomidate to enhance TI and block LTP in fl-α5 (WT), global-α5-KO (gl-α5-KO), and CA1-pyr-α5-KO mice. Etomidate suppressed LTP in slices from WT and CA1-pyr-α5-KO but not gl-α5-KO mice. There was a trend toward reduced TI in both gl-α5-KO and CA1-pyr-α5-KO mice, but etomidate enhanced TI to similar levels in all genotypes. The dissociation between effects of etomidate on TI and LTP in gl-α5-KO mice indicates that increased TI in pyramidal neurons is not the mechanism by which etomidate impairs LTP and memory. Rather, the ability of etomidate to block LTP in WT and CA1-pyr-α5-KO mice, but not in gl-α5-KO mice, points toward α5-GABAARs on nonpyramidal cells as the essential effectors controlling plasticity in this in vitro model of learning and memory.
Keywords: GABAA receptor; LTP; learning and memory; mechanisms of anesthesia.
Copyright © 2015 the authors 0270-6474/15/359707-10$15.00/0.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Etomidate blocks LTP and impairs learning but does not enhance tonic inhibition in mice carrying the N265M point mutation in the beta3 subunit of the GABA(A) receptor.Neuropharmacology. 2015 Jun;93:171-178. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.01.011. Epub 2015 Feb 11. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 25680234 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal β2-GABAA receptors mediate LTP suppression by etomidate and contribute to long-lasting feedback but not feedforward inhibition of pyramidal neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2021 Oct 1;126(4):1090-1100. doi: 10.1152/jn.00303.2021. Epub 2021 Aug 18. J Neurophysiol. 2021. PMID: 34406874 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha5GABAA receptors mediate the amnestic but not sedative-hypnotic effects of the general anesthetic etomidate.J Neurosci. 2006 Apr 5;26(14):3713-20. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5024-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16597725 Free PMC article.
-
Selective inhibition of extra-synaptic α5-GABAA receptors by S44819, a new therapeutic agent.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Oct;125:353-364. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.08.012. Epub 2017 Aug 12. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28807671
-
The Application and Pharmaceutical Development of Etomidate: Challenges and Strategies.Mol Pharm. 2024 Dec 2;21(12):5989-6006. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.4c00325. Epub 2024 Nov 4. Mol Pharm. 2024. PMID: 39495089 Review.
Cited by
-
Negative Allosteric Modulation of Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid A Receptors at α5 Subunit-Containing Benzodiazepine Sites Reverses Stress-Induced Anhedonia and Weakened Synaptic Function in Mice.Biol Psychiatry. 2022 Aug 1;92(3):216-226. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2021.11.024. Epub 2021 Dec 15. Biol Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35120711 Free PMC article.
-
New insights in the systemic and molecular underpinnings of general anesthetic actions mediated by γ-aminobutyric acid A receptors.Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2016 Aug;29(4):447-53. doi: 10.1097/ACO.0000000000000358. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2016. PMID: 27168087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relevance of Cortical and Hippocampal Interneuron Functional Diversity to General Anesthetic Mechanisms: A Narrative Review.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2022 Jan 26;13:812905. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2021.812905. eCollection 2021. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35153712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Control of contextual memory through interneuronal α5-GABAA receptors.PNAS Nexus. 2023 Apr 11;2(4):pgad065. doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgad065. eCollection 2023 Apr. PNAS Nexus. 2023. PMID: 37056471 Free PMC article.
-
Bidirectional regulation of distinct memory domains by α5-subunit-containing GABAA receptors in CA1 pyramidal neurons.Learn Mem. 2020 Sep 15;27(10):423-428. doi: 10.1101/lm.052084.120. Print 2020 Oct. Learn Mem. 2020. PMID: 32934095 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc. 1995;57:289–300.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
