Strain echocardiography identifies impaired longitudinal systolic function in patients with septic shock and preserved ejection fraction
- PMID: 26134971
- PMCID: PMC4487964
- DOI: 10.1186/s12947-015-0025-4
Strain echocardiography identifies impaired longitudinal systolic function in patients with septic shock and preserved ejection fraction
Abstract
Background: Myocardial dysfunction is recognized in sepsis. We hypothesized that mechanical left (LV) and right (RV) ventricular function analysed using 2-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography in a cohort of early severe sepsis or septic shock patients, would be different to that of a group of critically ill, non-septic patients.
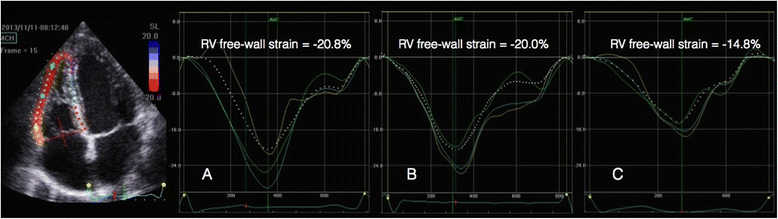
Methods: Critically ill adult patients with early, severe sepsis/septic shock (n = 48) and major trauma patients with no sepsis (n = 24) were included retrospectively, as well as healthy controls (n = 16). Standard echocardiographic examinations, including right (RV) left (LV) volumes and mitral, aortic and pulmonary vein Doppler flow profiles, were retrospectively identified and the studies were then reanalysed for assessment of myocardial strain using speckle-tracking echocardiography. Endocardial tracing of the LV was performed in apical four-chamber (4-Ch), two-chamber (2-Ch), apical long-axis (3-Ch) and apical views of RV determining the longitudinal LV and RV free wall strain in each subject.
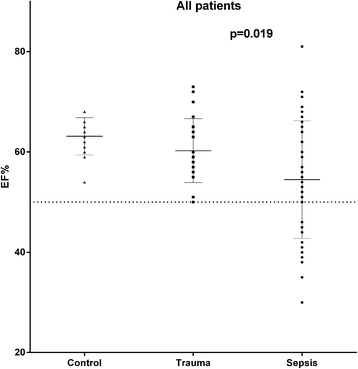
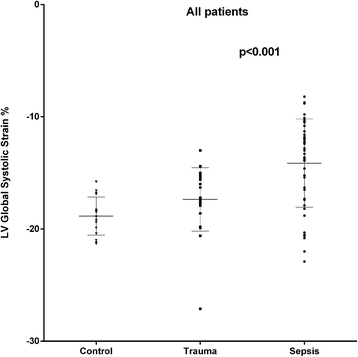
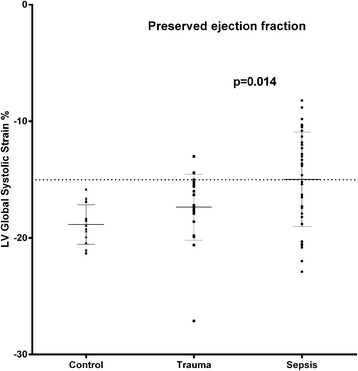
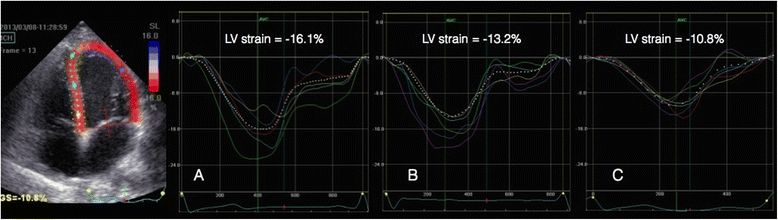
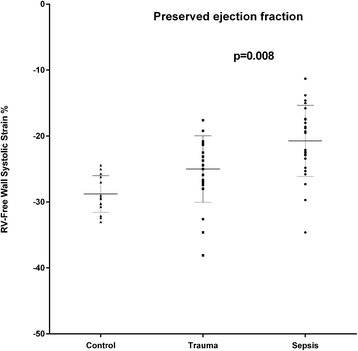
Results: In septic patients, heart rate was significantly higher (p = 0.009) and systolic (p < 0.001) and mean arterial pressures (p < 0.001), as well as systemic vascular resistance (p < 0.001) were significantly lower when compared to the non-septic trauma group. Ninety-three per cent of the septic patients and 50% of the trauma patients were treated with norepinephrine (p < 0.001). LV ejection fraction (LVEF) was lower in the septic patients (p = 0.019). In septic patients with preserved LVEF (>50%, n = 34), seventeen patients (50%) had a depressed LV global longitudinal function, defined as a LV global strain > -15%, compared to two patients (8.7%) in the non-septic group (p = 0.0014). In septic patients with preserved LVEF, LV global and RV free wall strain were 14% (p = 0.014) and 17% lower (p = 0.008), respectively, compared to the non-septic group with preserved LVEF. There were no significant differences between groups with respect to LV end-diastolic or end-systolic volumes, stroke volume, or cardiac output. There were no signs of diastolic dysfunction from the mitral or pulmonary vein Doppler profiles in the septic patients.
Conclusions: LV and RV systolic function is impaired in critically ill patients with early septic shock and preserved LVEF, as detected by Speckle-tracking 2D echocardiography. Strain imaging may be useful in the early detection of myocardial dysfunction in sepsis.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

