Population Pharmacokinetics of an Indian F(ab')2 Snake Antivenom in Patients with Russell's Viper (Daboia russelii) Bites
- PMID: 26135318
- PMCID: PMC4489840
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003873
Population Pharmacokinetics of an Indian F(ab')2 Snake Antivenom in Patients with Russell's Viper (Daboia russelii) Bites
Abstract
Background: There is limited information on antivenom pharmacokinetics. This study aimed to investigate the pharmacokinetics of an Indian snake antivenom in humans with Russell's viper bites.
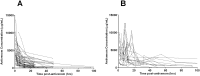
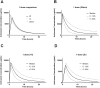
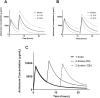
Methods/principal findings: Patient data and serial blood samples were collected from patients with Russell's viper (Daboia russelii) envenoming in Sri Lanka. All patients received Indian F(ab')2 snake antivenom manufactured by VINS Bioproducts Ltd. Antivenom concentrations were measured with sandwich enzyme immunoassays. Timed antivenom concentrations were analysed using MONOLIXvs4.2. One, two and three compartment models with zero order input and first order elimination kinetics were assessed. Models were parameterized with clearance (CL), intercompartmental clearance (Q), central compartment volume (V) and peripheral compartment volume (VP). Between-subject-variability (BSV) on relative bioavailability (F) was included to account for dose variations. Covariates effects (age, sex, weight, antivenom batch, pre-antivenom concentrations) were explored by visual inspection and in model building. There were 75 patients, median age 57 years (40-70 y) and 64 (85%) were male. 411 antivenom concentration data points were analysed. A two compartment model with zero order input, linear elimination kinetics and a combined error model best described the data. Inclusion of BSV on F and weight as a covariate on V improved the model. Inclusion of pre-antivenom concentrations or different batches on BSV of F did not. Final model parameter estimates were CL,0.078 L h(-1), V,2.2L, Q,0.178 L h(-1) and VP,8.33L. The median half-life of distribution was 4.6 h (10-90%iles:2.6-7.1 h) and half-life of elimination, 140 h (10th-90th percentilesx:95-223h).
Conclusion: Indian F(ab')2 snake antivenom displayed biexponential disposition pharmacokinetics, with a rapid distribution half-life and more prolonged elimination half-life.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neurotoxicity in Russell's viper (Daboia russelii) envenoming in Sri Lanka: a clinical and neurophysiological study.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2016 Jun;54(5):411-9. doi: 10.3109/15563650.2016.1143556. Epub 2016 Feb 29. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2016. PMID: 26923566
-
Phylovenomics of Daboia russelii across the Indian subcontinent. Bioactivities and comparative in vivo neutralization and in vitro third-generation antivenomics of antivenoms against venoms from India, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka.J Proteomics. 2019 Sep 15;207:103443. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2019.103443. Epub 2019 Jul 17. J Proteomics. 2019. PMID: 31325606
-
An open, randomized comparative trial of two antivenoms for the treatment of envenoming by Sri Lankan Russell's viper (Daboia russelii russelii).Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2001 Jan-Feb;95(1):74-80. doi: 10.1016/s0035-9203(01)90339-6. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2001. PMID: 11280073 Clinical Trial.
-
Hypopituitarism following envenoming by Russell's vipers (Daboia siamensis and D. russelii) resembling Sheehan's syndrome: first case report from Sri Lanka, a review of the literature and recommendations for endocrine management.QJM. 2011 Feb;104(2):97-108. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcq214. Epub 2010 Nov 28. QJM. 2011. PMID: 21115460 Review.
-
Proteomic analysis reveals geographic variation in venom composition of Russell's Viper in the Indian subcontinent: implications for clinical manifestations post-envenomation and antivenom treatment.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2018 Oct;15(10):837-849. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2018.1528150. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2018. PMID: 30247947 Review.
Cited by
-
Varespladib (LY315920) Appears to Be a Potent, Broad-Spectrum, Inhibitor of Snake Venom Phospholipase A2 and a Possible Pre-Referral Treatment for Envenomation.Toxins (Basel). 2016 Aug 25;8(9):248. doi: 10.3390/toxins8090248. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27571102 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Efficacy of Antivenom and Varespladib in Neutralising Chinese Russell's Viper (Daboia siamensis) Venom Toxicity.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Jan 11;15(1):62. doi: 10.3390/toxins15010062. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36668882 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic antibodies block receptor binding and current-inhibiting effects of α-cobratoxin from Naja kaouthia.Protein Sci. 2022 May;31(5):e4296. doi: 10.1002/pro.4296. Protein Sci. 2022. PMID: 35481650 Free PMC article.
-
Cost of Manufacturing for Recombinant Snakebite Antivenoms.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Jul 10;8:703. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00703. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32766215 Free PMC article.
-
A Single Dose of Viperfav(TM) May Be Inadequate for Vipera ammodytes Snake Bite: A Case Report and Pharmacokinetic Evaluation.Toxins (Basel). 2016 Aug 19;8(8):244. doi: 10.3390/toxins8080244. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27548220 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gawarammana IB, Kularatne SAM, Dissanayake WP, et al. Parallel infusion of hydrocortisone ñ chlorpheniramine bolus injection to prevent acute adverse reactions to antivenom for snakebites. Medical Journal of Australia 2004; 180: 20–3. - PubMed
-
- de Silva HA, Pathmeswaran A, Ranasinha CD, Jayamanne S, Samarakoon SB, Hittharage A, Kalupahana R, Ratnatilaka GA, Uluwatthage W, Aronson JK, Armitage JM, Lalloo DG, de Silva HJ. Low-dose adrenaline, promethazine, and hydrocortisone in the prevention of acute adverse reactions to antivenom following snakebite: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. PLoS Med 2011; 8: e1000435. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gutierrez JM, Leon G, Lomonte B. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic relationships of immunoglobulin therapy for envenomation. ClinPharmacokinet 2003; 42: 721–41. - PubMed
-
- Ariaratnam CA, Meyer WP, Perera G, Eddleston M, Kuleratne SA, Attapattu W, Sheriff R, Richards AM, Theakston RD, Warrell DA. A new monospecific ovine Fab fragment antivenom for treatment of envenoming by the Sri Lankan Russell's viper (Daboia Russelii Russelii): a preliminary dose-finding and pharmacokinetic study. American Journal of Tropical Medicine & Hygiene 1999; 61: 259–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

