Febuxostat pretreatment attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via mitochondrial apoptosis
- PMID: 26136232
- PMCID: PMC4489215
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-015-0578-x
Febuxostat pretreatment attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via mitochondrial apoptosis
Abstract
Background: Febuxostat is a selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase (XO). XO is a critical source of reactive oxygen species (ROS) during myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. Inhibition of XO is therapeutically effective in I/R injury. Evidence suggests that febuxostat exerts antioxidant effects by directly scavenging ROS. The present study was performed to investigate the effects of febuxostat on myocardial I/R injury and its underlying mechanisms.
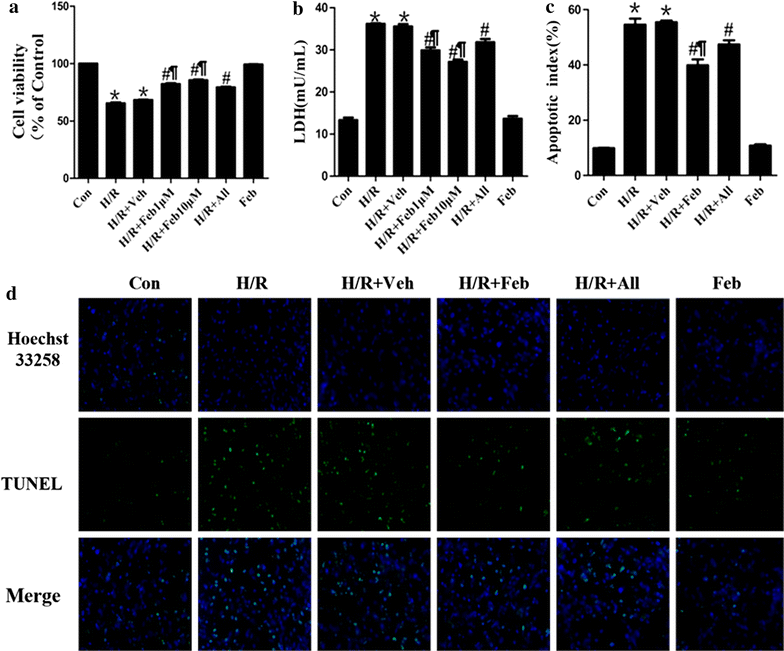
Methods: We utilized an in vivo mouse model of myocardial I/R injury and an in vitro neonatal rat cardiomyocyte (NRC) model of hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) injury. Mice were randomized into five groups: Sham, I/R (I/R + Vehicle), I/R + FEB (I/R + febuxostat), AL + I/R (I/R + allopurinol) and FEB (febuxostat), respectively. The I/R + FEB mice were pretreated with febuxostat (5 mg/kg; i.p.) 24 and 1 h prior to I/R. NRCs received febuxostat (1 and 10 µM) at 24 and 1 h before exposure to hypoxia for 3 h followed by reoxygenation for 3 h. Cardiac function, myocardial infarct size, serum levels of creatine kinase (CK) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and myocardial apoptotic index (AI) were measured in order to ascertain the effects of febuxostat on myocardial I/R injury. Hypoxia/reperfusion (H/R) injury in NRCs was examined using MTT, LDH leakage assay and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay. The underlying mechanisms were determined by measuring ROS production, mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm), and expression of cytochrome c, cleaved caspases as well as Bcl-2 protein levels.
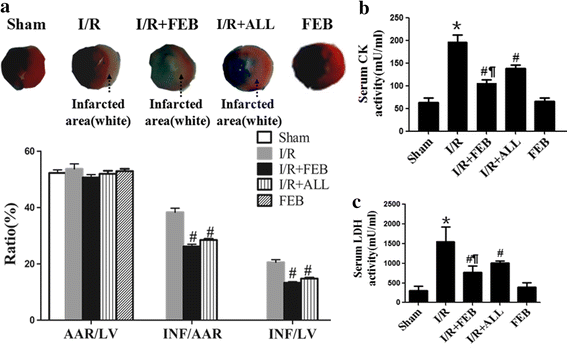
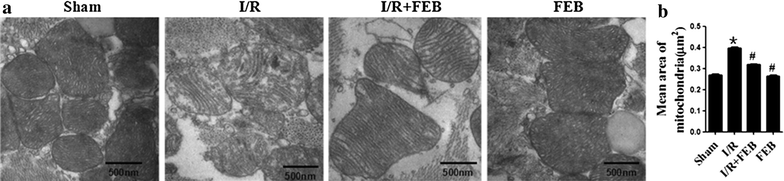
Results: Myocardial I/R led to an elevation in the myocardial infarct size, serum levels of CK and LDH, cell death and AI. Furthermore, I/R reduced cardiac function. These changes were significantly attenuated by pretreatment with febuxostat and allopurinol, especially by febuxostat. Febuxostat also protected the mitochondrial structure following myocardial I/R, inhibited H/R-induced ROS generation, stabilized the ΔΨm, alleviated cytosolic translocation of mitochondrial cytochrome C, inhibited activation of caspase-3 and -9, upregulated antiapoptotic proteins and downregulated proapoptotic proteins.
Conclusions: This study revealed that febuxostat pretreatment mediates the cardioprotective effects against I/R and H/R injury by inhibiting mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

