Marriage Trajectories and Health Risk Behaviors Throughout Adulthood Among Urban African Americans
- PMID: 26136611
- PMCID: PMC4484881
- DOI: 10.1177/0192513X11432429
Marriage Trajectories and Health Risk Behaviors Throughout Adulthood Among Urban African Americans
Abstract
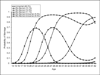
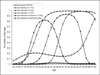
Although previous studies have identified a protective effect of marriage on risky health behaviors, gaps remain in our understanding of how marriage improves health, particularly among African Americans. This study uses longitudinal data to take selection into account and examines whether marital trajectories that incorporate timing, stability, and duration of marriage affect health risk behaviors among a community cohort of urban African Americans followed for 35 years (N = 1,049). For both men and women, we find six marital trajectories. Men and women in consistently married trajectories are less likely to smoke, drink heavily (women only), and use illegal drugs than those in unmarried or previously married trajectories. Late marrying men do not fare worse in midlife than men in earlier marrying trajectories, but late marrying women show increased risk of midlife drug use. Results suggest policies supporting marriage may have an impact on health but only if stable unions are achieved.
Keywords: African Americans; health; longitudinal studies; marriage; substance use.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson E. Code of the street: Decency, violence, and the moral life of the inner city. New York, NY: W. W. Norton; 2000.
-
- Axinn WG, Thorton A. The influence of parental resources on the timing of the transition to marriage. Social Science Research. 1992;21:261–285.
-
- Bachman JG, O’Malley PM, Schulenberg JE, Johnston LD, Bryant AL, Merline AC. The decline of substance use in young adulthood: Changes in social activities, roles, and beliefs. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum; 2002.
-
- Bachman JG, Wadsworth KN, O’Malley PM, Johnston LD, Schulenberg JE. Smoking, drinking, and drug use in young adulthood: The impacts of new freedoms and new responsibilities. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum; 1997.
-
- Berkman LF, Glass T. Social integration, social networks, social support, and health. In: Berkman LF, Kawachi I, editors. Social epidemiology. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 2000. pp. 137–173.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources